Global Biochar Market Forecast
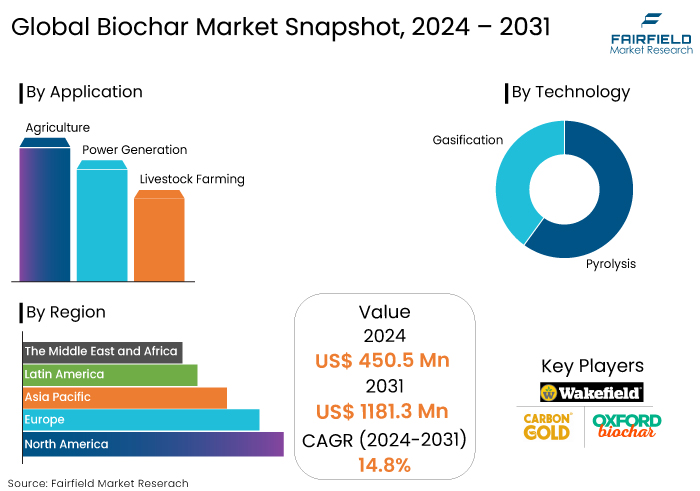
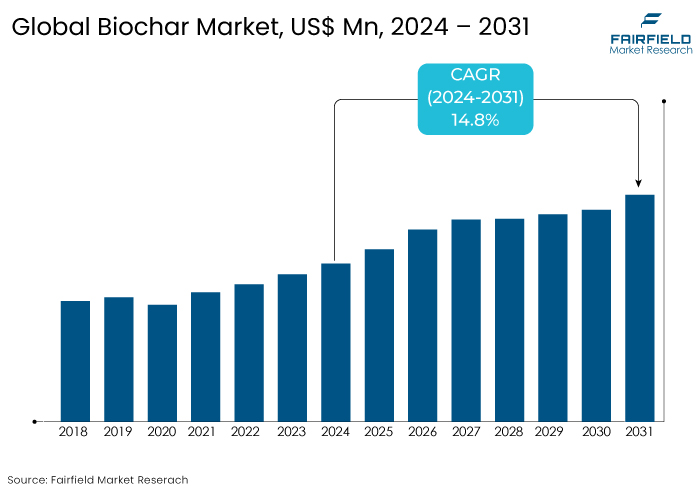
- The biochar market is projected to reach a size of US$1181.3 Mn by 2031, showing significant growth from the US$450.5 Mn achieved in 2024.
- The market for biochar is expected to show a significant expansion rate, with an estimated CAGR of 14.8% during the period from 2024 to 2031.
Biochar Market Insights
- The global biochar market is projected to grow significantly driven by increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices.
- Biochar is crucial in carbon sequestration helping mitigate climate change by locking carbon in the soil.
- Biochar improves soil health by enhancing nutrient retention, moisture management, and microbial activity.
- Government initiatives and policies promoting sustainable practices boost biochar adoption particularly in North America and Europe.
- Continuous research and development are essential for improving production methods and expanding biochar applications.
- Developing regions increasingly recognize biochar's benefits presenting growth opportunities for the market.
- Market growth faces high production costs and varying regulatory standards across regions.
- Partnerships among producers, researchers, and agricultural stakeholders are vital for overcoming barriers and promoting biochar's benefits.
A Look Back and a Look Forward - Comparative Analysis
The biochar market has seen significant growth driven by rising awareness of sustainable agriculture, carbon sequestration, and waste management. Pre-2023, the market expanded steadily as biochar gained recognition for improving soil health, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancing crop yields.
Increasing interest in organic farming and environmental sustainability particularly in Europe and North America contributed to its adoption. The global market experienced a CAGR of around 10% between 2019 and 2023.
The biochar market is projected to grow at an accelerated pace post-2024 driven by the increasing emphasis on carbon management strategies and the use of biochar in industries beyond agriculture such as construction and energy production.
Government initiatives promoting carbon-neutral technologies and growing demand in developing regions like Asia Pacific will likely to fuel market expansion. Analysts expect a CAGR of around 13-15% from 2024 to 2031 as the global shift toward climate-friendly practices continues to promote the adoption of biochar for its environmental benefits.
Key Growth Determinants
- Rising Environmental Concern is Uplifting the Usage of Biochar
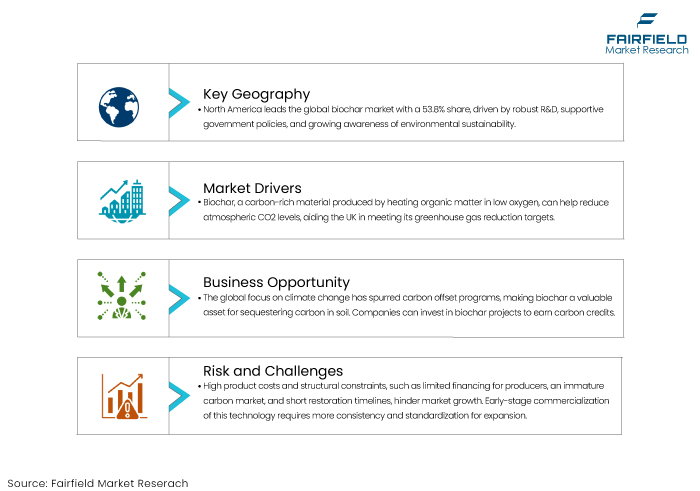
Biochar is a carbon-rich material made by heating organic matter in low oxygen conditions. It may reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, thus helping the UK meet its greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets.
During pyrolysis, around 50% of the carbon in the biomass is converted into Biochar. Around two-thirds of the remaining 50% can be released as helpful energy. They release CO2 and methane back into the atmosphere. They can also contaminate local ground and surface water. Using these materials to produce biochar removes them from a pollutant cycle and can be extracted from this biomass as a by-technology for energy production.
Two bioenergy technologies are produced during biochar production processes including syngas and bio-oil. In certain instances, the energy available from the syngas produced can act to self-sustain the Biochar formation reducing fossil fuel inputs, or it can be used in turbines to produce electricity directly.
Biochar can be used on sites where the land is contaminated with heavy metals from prior industrial use. Biochar acts as an adsorbent, binding metal pollutants to its surface, immobilizing them, and reducing their toxicity over time. In addition, Biochar and brown coal waste (BCW) have lower contaminants. These also have been shown to provide additional sustainability and net cost benefits.
- Burgeoning use of Biochar in Animal Feed to Stimulate the Demand for Biochar
Biochar-based fertilizers, which combine traditional fertilizers with biochar as a nutrient carrier are promising in agronomy. Using biochar as a feed additive for animals shows benefits in terms of overall growth, egg yield, and endo-toxicant mitigation.
Biochar enhances anaerobic digestion operations, primarily for biogas generation and upgrading, performance and sustainability, and the mitigation of inhibitory impurities. Incomposts and biochar control the release of greenhouse gases and enhance microbial activity.
Co-composted biochar improves soil properties and enhances crop productivity. Livestock-manure-derived biochar is one of the key products obtained from the pyrolysis of livestock manure. Discharges of manure lead to environmental problems such as odors rooting in the emission of toxic gases and pollution of waterways because of leaching and runoff of nurtures and heavy metals.
Biocharprepared by livestock manure is the solid carbonaceous residue from the pyrolysis of livestock manure. The conversion of livestock manure to biochar has various potential economic effects, including agricultural waste reduction, fuel production, and carbon sink.
Key Growth Barriers
- High Cost and Lack of Knowledge about Manufacturing Process
The cost of such products and underlying structural constraints such as a shortage of finance for producers, an immature carbon market, and short timescales for mining land restoration bonds continue to impede the market growth. While the commercialization of this technology is still in its early stages, this hard-to-sell technology needs more consistency and standardization to ensure market expansion.
Biomass is used as the feedstock in the pyrolysis reactor, which has a set heating and gas flow rate, residence duration, and temperature. Following that, Biochar can be created. During pyrolysis, most of the Ca, K, P, Mg, and plant micronutrients, as well as half of the N and S in the feedstock are retained in Biochar. There are certain byproducts of this process such as gas and oil.
When Biochar is applied to agricultural land, several prior research identified the drawbacks such as loss of land due to erosion, soil compaction during the application, and reduction in worm life rates. These factors create a negative impact on the environment and could affect the market.
- Lack of Awareness about the Benefits of Biochar
The global biochar market faces a significant restraint in the form of a lack of awareness regarding the benefits of biochar particularly in emerging markets. Biochar, a carbon-rich product derived from the pyrolysis of organic materials offers numerous environmental and agricultural advantages. These advantages include soil improvement, carbon sequestration, and waste management.
The limited dissemination of information and education on Biochar's potential benefits hampers its widespread adoption especially in developing economies.
In emerging markets, where agricultural practices often play a pivotal role in livelihoods, the need for more awareness about Biochar's positive impacts on soil fertility and crop yield acts as a barrier to market growth. Farmers and stakeholders may need to be made aware of the potential long-term benefits of incorporating Biochar into their farming practices.
The complex nature of biochar production and application methods can contribute to the reluctance to embrace this sustainable solution. Governments, non-governmental organizations, and industry players must collaboratively undertake awareness campaigns and educational initiatives to enlighten farmers, policymakers, and the general public about the advantages of Bbiochar.
Biochar Market Trends and Opportunities
- Biochar’s Ability to Sequester Carbon in the Soil
The global emphasis on mitigating climate change has led to the establishment of carbon offset programs. Biochar, with its ability to sequester carbon in the soil becomes a valuable asset in these programs. Companies and industries seeking to offset carbon emissions can invest in Biochar projects to earn carbon credits.
Biochar production is often linked to bioenergy processes, where biomass is used to generate energy, and biochar is produced as a byproduct. Investments in renewable energy projects that utilize Biocharcan are eligible for carbon credits, creating an additional revenue stream for Biochar producers.
Many governments worldwide are introducing incentives and regulations to encourage adopting sustainable practices and carbon sequestration technologies. In regions where Biochar is recognized as a valuable tool for carbon capture, producers can benefit from government programs offering financial incentives or credits for adopting Biochar technologies.
The emergence of voluntary carbon markets presents an opportunity for Biochar projects to attract investment from organizations and individuals seeking to offset their carbon footprint voluntarily. Biochar producers can participate in these markets, offering carbon credits as a tangible and marketable environmental benefit.
- Government Backing Propels Growth of Voluntary Carbon Markets
A significant hurdle for companies entering voluntary carbon markets is the fragmented landscape encompassing multiple standards, rating agencies, projects, and brokers. This diversity poses challenges in distinguishing high-quality from low-quality credits, compounded by time-consuming over-the-counter trades, deterring participation.
Since the closure of CCX, centralized trading platforms have been scarce and relatively small-scale, impeding market efficiency. However, governments are pivotal in fostering market centralization within their jurisdictions. Initiatives like Australia's carbon exchange and Japan's voluntary market aim to establish centralized trading platforms, enhancing transparency and efficiency.
Governments leverage their unique legitimacy and regulatory authority to drive credit supply and trade infrastructure toward centralization in voluntary markets. Enhancing carbon credit quality and bolstering the removal credit supply stand as key opportunities for government support in voluntary markets.
Government involvement, as seen in Australia and Japan has unified markets around government-issued units like ACCU and J-Credit reducing supply heterogeneity and aiding corporations in identifying credit supply patterns efficiently.
Governments have the potential to steer capital towards specific projects in voluntary carbon markets. By focusing on strategic priorities, governments can narrow eligibility criteria for supply, targeting particular technologies, project models, or geographic locations.
How Does Regulatory Scenario Shape this Industry?
The regulatory scenario is playing a pivotal role in shaping the biochar market, particularly as governments and environmental agencies worldwide emphasize sustainability, carbon reduction, and climate change mitigation.
In regions like Europe and North America, stringent environmental regulations are encouraging the adoption of carbon sequestration technologies including biochar to meet climate targets. The European Union, for example has been promoting biochar as part of its circular economy and carbon reduction strategies offering incentives and subsidies for biochar projects that contribute to soil enhancement and carbon storage.
The growing recognition of biochar’s role in sustainable agriculture and waste management has led to favorable policies supporting its use in soil amendments. However, the regulatory framework for biochar varies globally, with some regions lacking clear guidelines on production standards and quality control.
As the market grows, there is a push for harmonized regulations that set standards for biochar production, usage, and certification, ensuring its safe and effective application. These evolving regulations are expected to create a more structured and supportive environment, promoting market growth by providing clear pathways for commercialization and large-scale adoption.
Segments Covered in the Report
- Pyrolysis Technology Takes the Lead
Pyrolysis is a thermal conversion technique conducted within the 300–800 ◦C temperature range, primarily optimizing biochar production. This technology type accounts for 87.9% of the total market share in 2024. This process occurs at atmospheric pressure, featuring extended residence times and low heating rates.
Various reactor types including agitated drum sand rotating kilns, wagon reactors, and paddle pyrolysis kilns have been employed for biochar generation through slow pyrolysis. High biochar yields are typically achieved when utilizing feedstock with elevated lignin and ash content and larger particle sizes. These characteristics enhance Biochar yield by promoting cracking reactions that reduce bio-oil production.
- Agriculture is the Leading Application of Biochar
Agriculture sector dominates the market due to biochar’s significant benefits in improving soil health, enhancing crop yields, and promoting sustainable farming practices and accounts for 69.2% of the market share. When applied to soil, biochar improves its structure, enhances moisture retention, and increases nutrient availability. Consequently, making it an ideal solution for agriculture particularly in regions with poor soil quality or water scarcity.
Biochar’s porous nature helps retain fertilizers and prevent nutrient leaching, which boosts plant growth and reduces the need for chemical inputs, supporting organic and regenerative farming practices.
Regional Analysis
- North America Biochar Market Retains Top Position
North America is dominant in the global biochar market accounting for 53.8% of the market share. This regional market growth is driven by several interrelated factors, including strong research and development initiatives, supportive government policies, and increasing awareness of environmental sustainability.
The region is home to numerous universities, research institutions, and private companies focused on biochar technology and its applications. This concentration of expertise fosters innovation in biochar production methods, enhancing its efficiency and effectiveness in agricultural and environmental applications.
Advanced research on biochar’s benefits, such as soil enhancement, carbon sequestration, and waste management, has propelled its adoption in North America. North America governments, particularly in the United States and Canada have implemented supportive policies promoting renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and carbon management.
Incentives, grants, and subsidies for biochar projects encourage farmers and businesses to adopt biochar as a viable solution for improving soil health and mitigating climate change.
Fairfield’s Competitive Landscape Analysis
The biochar market is characterized by a competitive landscape with several key players focused on innovation and sustainability. Prominent companies, including Biochar Now, Pacific Biochar, and CharGrow, are leading the market by offering high-quality biochar products and developing advanced production technologies.
Companies invest in research and development to enhance biochar's effectiveness in agriculture, soil remediation, and carbon sequestration. Numerous small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are emerging, providing niche biochar solutions tailored to specific agricultural and industrial applications.
Collaborations between agricultural stakeholders, research institutions, and biochar producers are fostering growth in the market. As awareness of biochar’s ebiochar'stal benefits increases, competition is expected to intensify, driving innovation and expanding market opportunities across various sectors.
Key Market Companies
- Oxford Biochar
- Circular Carbon GmbH
- Carbon Gold Ltd
- Wakefield Biochar
- Green Man Char
- Carbo Culture
- Airex Energy
- Carbonis GmbH & Co. KG
- American BioChar Company
- VGrid Energy Systems
Recent Industry Developments
- July 2023 -
Airex Energy, Groupe Rémabec, and SUEZ partnered to create Canada's first industrial biochar production plant in Port-Cartier, Québec. The plant's first phase will be finalized in 2024, with an initial Production capacity of 10,000 tons per year.
- August 2023 –
Carbo Culture's first industrial pilot facility opens near Helsinki, Finland, demonstrating efficient and scalable biochar carbon removal. The facility, named 'R3, Reactor 3,' is funded by the European Innovation Council, and it uses a method called biochar carbon removal (BCR) to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere permanently.
An Expert’s Eye
- Continuous advancements in production methods and applications are vital in improving biochar’s effectiveness and commercial viability.
- Increasing awareness of environmental benefits, particularly in North America and Europe, aids the market.
- Educating farmers and stakeholders about the benefits of biochar is necessary to enhance its adoption and utilization in various agricultural practices.
- Collaborations between biochar producers, agricultural organizations, and research institutions will be key to overcoming market challenges and driving innovation.
Global Biochar Market is Segmented as-
By Technology
- Pyrolysis
- Gasification
By Application
- Agriculture
- Power Generation
- Livestock Farming
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
1. Executive Summary
1.1. Global Biochar Market Snapshot
1.2. Key Market Trends
1.3. Future Projections
1.4. Analyst Recommendations
2. Market Overview
2.1. Market Definitions and Segmentations
2.2. Market Dynamics
2.2.1. Drivers
2.2.1.1. Driver A
2.2.1.2. Driver B
2.2.1.3. Driver C
2.2.2. Restraints
2.2.2.1. Restraint 1
2.2.2.2. Restraint 2
2.2.3. Market Opportunities Matrix
2.3. Value Chain Analysis
2.4. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.5. Covid-19 Impact Analysis
2.5.1. Pre-Covid and Post-Covid Scenario
2.5.2. Supply Impact
2.5.3. Demand Impact
2.6. Government Regulations
2.7. Technology Landscape
2.8. Economic Analysis
2.9. PESTLE
3. Production Output and Trade Statistics, 2019-2023
3.1. Regional Production Statistics
3.1.1. North America
3.1.2. Europe
3.1.3. Asia Pacific
3.1.4. Latin America
3.1.5. Middle East & Africa
4. Price Trends Analysis and Future Projects, 2019-2031
4.1. Key Highlights
4.2. Prominent Factors Affecting Prices
4.3. By Region
5. Global Biochar Market Outlook, 2019-2031
5.1. Global Biochar Market Outlook, by Technology, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
5.1.1. Key Highlights
5.1.1.1. Pyrolysis
5.1.1.2. Gasification
5.1.1.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
5.2. Global Biochar Market Outlook, by Application, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
5.2.1. Key Highlights
5.2.1.1. Power Generation
5.2.1.2. Agriculture
5.2.1.3. Livestock Farming
5.2.1.4. Misc.
5.3. Global Biochar Market Outlook, by Region, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
5.3.1. Key Highlights
5.3.1.1. North America
5.3.1.2. Europe
5.3.1.3. Asia Pacific
5.3.1.4. Latin America
5.3.1.5. Middle East & Africa
5.3.2. BPS/Market Attractiveness Analysis
6. North America Biochar Market Outlook, 2019-2031
6.1. North America Biochar Market Outlook, by Technology, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
6.1.1. Key Highlights
6.1.1.1. Pyrolysis
6.1.1.2. Gasification
6.1.1.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
6.2. North America Biochar Market Outlook, by Application, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
6.2.1. Key Highlights
6.2.1.1. Power Generation
6.2.1.2. Agriculture
6.2.1.3. Livestock Farming
6.2.1.4. Misc.
6.3. North America Biochar Market Outlook, by Country, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
6.3.1. Key Highlights
6.3.1.1. U.S.
6.3.1.2. Canada
6.3.2. BPS/Market Attractiveness Analysis
7. Europe Biochar Market Outlook, 2019-2031
7.1. Europe Biochar Market Outlook, by Technology, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
7.1.1. Key Highlights
7.1.1.1. Pyrolysis
7.1.1.2. Gasification
7.1.1.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
7.2. Europe Biochar Market Outlook, by Application, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
7.2.1. Key Highlights
7.2.1.1. Power Generation
7.2.1.2. Agriculture
7.2.1.3. Livestock Farming
7.2.1.4. Misc.
7.3. Europe Biochar Market Outlook, by Country, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
7.3.1. Key Highlights
7.3.1.1. Germany
7.3.1.2. U.K.
7.3.1.3. Sweden
7.3.1.4. Russia
7.3.1.5. Rest of Europe
7.3.2. BPS/Market Attractiveness Analysis
8. Asia Pacific Biochar Market Outlook, 2019-2031
8.1. Asia Pacific Biochar Market Outlook, by Technology, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2018-2030
8.1.1. Key Highlights
8.1.1.1. Pyrolysis
8.1.1.2. Gasification
8.1.1.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
8.2. Asia Pacific Biochar Market Outlook, by Application, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
8.2.1. Key Highlights
8.2.1.1. Power Generation
8.2.1.2. Agriculture
8.2.1.3. Livestock Farming
8.2.1.4. Misc.
8.3. Asia Pacific Biochar Market Outlook, by Country, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
8.3.1. Key Highlights
8.3.1.1. China
8.3.1.2. Japan
8.3.1.3. South Korea
8.3.1.4. India
8.3.1.5. Australia
8.3.1.6. Rest of Asia Pacific
8.3.2. BPS/Market Attractiveness Analysis
9. Latin America Biochar Market Outlook, 2018 – 2030
9.1. Latin America Biochar Market Outlook, by Technology, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
9.1.1. Key Highlights
9.1.1.1. Pyrolysis
9.1.1.2. Gasification
9.1.1.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
9.2. Latin America Biochar Market Outlook, by Application, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
9.2.1. Key Highlights
9.2.1.1. Power Generation
9.2.1.2. Agriculture
9.2.1.3. Livestock Farming
9.2.1.4. Misc.
9.3. Latin America Biochar Market Outlook, by Country, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
9.3.1. Key Highlights
9.3.1.1. Brazil
9.3.1.2. Mexico
9.3.1.3. Rest of Latin America
9.3.2. BPS/Market Attractiveness Analysis
10. Middle East & Africa Biochar Market Outlook, 2019-2031
10.1. Middle East & Africa Biochar Market Outlook, by Technology, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
10.1.1. Key Highlights
10.1.1.1. Pyrolysis
10.1.1.2. Gasification
10.1.1.3. Hydrothermal Carbonization
10.2. Middle East & Africa Biochar Market Outlook, by Application, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
10.2.1. Key Highlights
10.2.1.1. Power Generation
10.2.1.2. Agriculture
10.2.1.3. Livestock Farming
10.2.1.4. Misc.
10.3. Middle East & Africa Biochar Market Outlook, by Country, Volume (Tons) and Value (US$ Mn), 2019-2031
10.3.1. Key Highlights
10.3.1.1. GCC
10.3.1.2. South Africa
10.3.1.3. Rest of Middle East & Africa
10.3.2. BPS/Market Attractiveness Analysis
11. Competitive Landscape
11.1. Company Market Share Analysis, 2022
11.2. Competitive Dashboard
11.3. Company Profiles
11.3.1. American BioChar Company
11.3.1.1. Company Overview
11.3.1.2. Product Portfolio
11.3.1.3. Financial Overview
11.3.1.4. Business Strategies and Development
(*Note: Above details would be available for below list of companies based on availability)
11.3.2. Green Man Char
11.3.3. Pacific Biochar
11.3.4. Carbonis GmbH & Co. KG
11.3.5. Airex Energy
11.3.6. Novocarbo GmbH
11.3.7. Biochar Industries
11.3.8. Carbon Gold
11.3.9. ArSta eco
11.3.10. Puro.earth
11.3.11. Farm2energy Pvt. Ltd.
11.3.12. Swiss Biochar
11.3.13. Skanefrö AB
12. Appendix
12.1. Research Methodology
12.2. Report Assumptions
12.3. Acronyms and Abbreviations
|
BASE YEAR |
HISTORICAL DATA |
FORECAST PERIOD |
UNITS |
|||
|
2022 |
|
2019 - 2022 |
2023 - 2030 |
Value: US$ Mn Volume: Tons |
||
|
REPORT FEATURES |
DETAILS |
|
Technology Coverage |
|
|
Application Coverage |
|
|
Geographical Coverage |
|
|
Leading Companies |
|
|
Report Highlights |
Market Estimates and Forecast, Market Dynamics, Industry Trends, Production Output, Trade Statistics, Prices Trend Analysis, Competition Landscape, Technology-, Application-, Region-, Country-wise Trends & Analysis, COVID-19 Impact Analysis (Demand and Supply), Key Market Trends |
