Global Digital Remittance Market Forecast
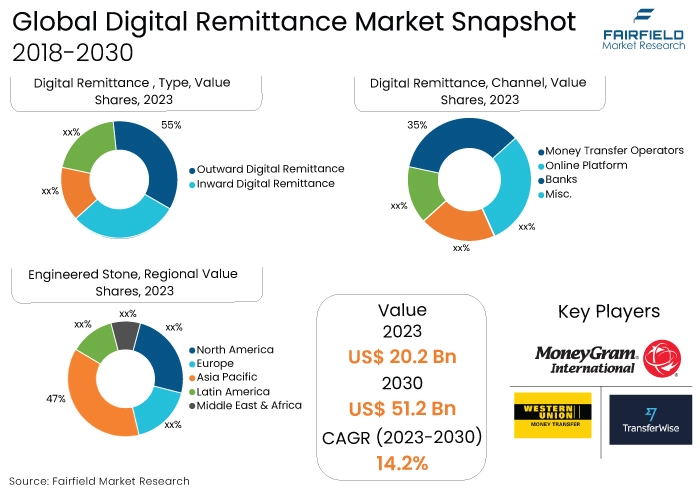
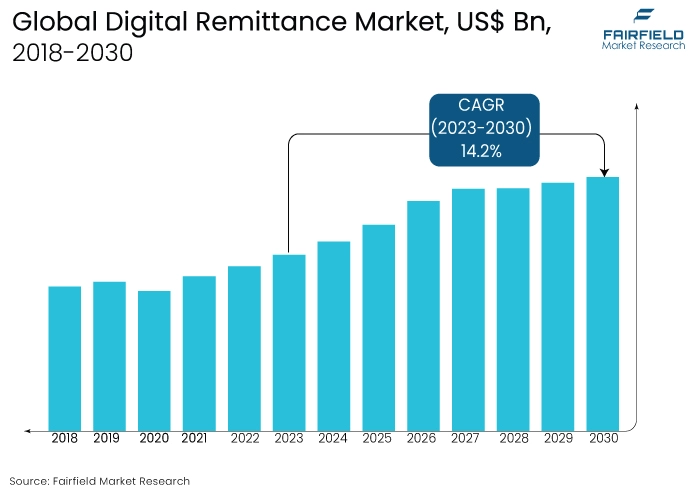
- Global digital remittance market size to reach US$51.2 Bn in 2030 from US$20.2 Bn in 2023
- Digital remittance market valuation projected to witness a CAGR of 14.2% during 2023-2030
Quick Report Digest
- The key trends anticipated to fuel the digital remittance market growth an increased international migration, globalisation, and the growing need for efficient cross-border transactions.
- Another major market trend expected to fuel the Digital Remittance market growth is Increased digitisation and automation, lower remittance fees, quicker transfer times, ease of use, and growing adoption of banking and financial services.
- The adoption of digital transfers offers advantages like faster transactions, reduced fees, real-time monitoring, and enhanced security. This industry is further propelled by the growing prevalence of smartphones and the accessibility of affordable internet services.
- In 2023, the outward digital remittance category dominated the industry. It addresses the significant needs of both individuals and businesses who transfer money across borders to assist family members, invest, or engage in international trade.
- In terms of market share for digital remittance globally, the money transfer operators segment is anticipated to dominate. Money transfer operators (MTOs) dominate a considerable portion of the remittance market owing to their well-established networks, extensive accessibility, and recognised brand recognition.
- In 2023, the personal category controlled the market. This segment commands a significant market share due to the large volume of personal transactions conducted regularly, typically influenced by factors such as international migration, educational pursuits, and providing financial assistance to family members.
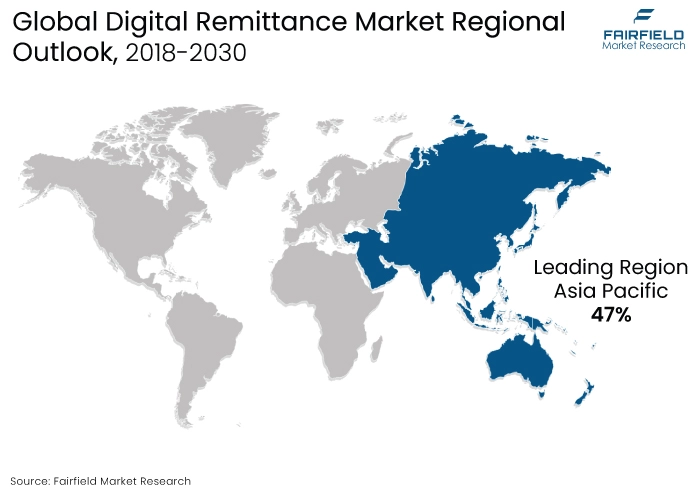
- The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to account for the largest share of the global digital remittance market, owing to Increasing income levels, enhanced financial infrastructure, and greater penetration of smartphones.
- The market for digital remittance is expanding in North America due to the region's benefits from a robust financial infrastructure, widespread internet and smartphone usage, and a substantial migrant population that frequently sends money back to their countries of origin.
A Look Back and a Look Forward - Comparative Analysis
The market for digital remittance has grown in popularity as a result of factors such as globalisation, increased international migration, and the widespread adoption of digital payment technologies. Companies within this market offer services enabling individuals and businesses to transfer money internationally, making it an essential component of the global financial system. This sector is marked by intense competition and continual technological innovation.
The market witnessed staggered growth during the historical period 2018 – 2022. This is due to the substantial growth of the major end-use application sectors such as small businesses, and others. However, in some applications, the demand for digital remittance has increased, including migrant labour workforce, personnel.
The growth of the market is further fuelled by regulatory efforts aimed at enhancing transparency among financial institutions, thereby improving data ecosystems and partnerships. Additionally, the rise in immigration rates from developing to developed countries, driven by opportunities for education and employment, is driving growth in the global digital remittance market.
Key Growth Determinants
- Rapid Growth in Urbanisation, and Cross-Border Transactions
The global population is experiencing rapid urbanisation and industrialisation, leading to the development of rural and semi-rural areas worldwide. According to the World Bank, the current urban population stands at 56% of the world's population, totaling 4.4 billion people, with projections indicating that this figure will more than double by 2050, with nearly 7 out of 10 individuals residing in cities. This trend is observable across the globe, with a growing proportion of people choosing urban living. In 2012, urban dwellers accounted for 52.5% of the population, a figure projected to increase to 56.9% by 2022.
Urbanisation rates vary between developed and developing regions, with 79.7% of the population living in urban areas in developed countries compared to 52.3% in developing nations. In the least developed countries (LDCs), urban populations remain a minority, constituting 35.8%. This migration trend is driven by individuals seeking employment opportunities, launching businesses, and pursuing job prospects across international borders and within various cities. Consequently, there has been a notable increase in cross-border transactions.
Traditionally, such transactions were predominantly conducted by large corporations and governmental entities. However, the emergence of digital platforms has democratised these transactions, facilitating a broad spectrum of microtransactions involving small-scale organisations, individual purchases, microloans, micropayments, and freelance work through contractual agreements.
Platforms like Kickstarter, Zopa, and Kiva have become instrumental in facilitating cross-border financial interactions. Kiva, for instance, has facilitated money transfers for over 1 million individuals across 190 countries. Kickstarter, a crowdfunding platform connecting entrepreneurs with backers interested in supporting their creative projects, has garnered the participation of 5.8 million individuals from 214 countries. Since its inception in 2009, Kickstarter has facilitated pledges totaling US$1 billion for 58,000 creative ventures.
- Rocketing Smartphone Sales
The burgeoning emphasis on digital remittance, driven by the rapid pace of digitalisation, is fuelling market expansion. According to the GSMA’s annual State of Mobile Internet Connectivity Report 2023 (SOMIC), over half of the global population, amounting to approximately 4.3 billion individuals, now owns smartphones.
Of the 4.6 billion people using mobile internet, nearly 4 billion utilize smartphones, constituting close to half of the world's population. Additionally, 600 million people, representing 8% of the global population, access the internet via feature phones. This widespread smartphone adoption underscores a growing preference for digital solutions in financial transactions.
Digital remittance platforms offer a convenient and efficient means of transferring money globally, eliminating the necessity for physical visits to traditional financial institutions. The increasing prevalence of smartphones and improved internet connectivity further bolster the market's growth trajectory. Moreover, users can easily access digital remittance services through intuitive mobile applications or websites, facilitating seamless international money transfers.
Furthermore, the digitisation of remittance processes enables real-time tracking and notifications, enhancing transparency and security in transactions. These features contribute to the ease of conducting remittances and support market expansion. Additionally, financial technology (FinTech) companies are channeling investments into innovative solutions, ensuring that digital remittance remains a preferred choice for users seeking simplicity and convenience in cross-border money transfers.
- Surge in International Transactions
International money transactions involve the direct transfer of funds to an individual's or company's overseas bank account. These transfers can be facilitated through banks, international money transfer services, online platforms, or specialised agents. Digital remittances offer faster and more efficient transfer options compared to traditional methods, leveraging new money movement networks and often bypassing correspondent banking channels.
For instance, in May 2022, the World Bank, a US-based international financial institution, projected a 4.2% increase in officially registered money transfers to low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), reaching $630 billion. This uptick in international transactions underscores the driving force behind the growth of the digital remittance market.
Major Growth Barriers
- Cybersecurity Risks Are Limiting Market Expansion
The growth of the digital remittance market is hampered by significant cybersecurity risks. Handling sensitive financial data makes these services prime targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities, leading to security breaches, data theft, and fraudulent activities. Such incidents not only cause financial losses for users but also damage the reputation of service providers, hindering market growth.
Cyber attacks, rated as the fifth top risk in 2020, have become increasingly common across public and private sectors. This trend persists in 2024, with IoT cyberattacks expected to double by 2025. The World Economic Forum’s 2020 Global Risk Report indicates a low detection rate of cybercrimes in the U.S., while Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that global cybercrime will cost companies $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, representing the largest transfer of economic wealth in history. Small businesses, in particular, are vulnerable, with 43% targeted by cyber attacks but only 14% adequately prepared for defense.
To address these risks, digital remittance companies must invest significantly in cybersecurity measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring. However, these investments increase operational costs and may reduce profit margins, affecting the competitiveness of digital remittance services.
Additionally, regulatory bodies are imposing stricter cybersecurity compliance requirements, necessitating ongoing adjustments and investments to meet evolving standards. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to legal consequences and penalties, further impeding market growth. Overall, the persistent and evolving nature of cybersecurity threats poses a significant challenge to the expansion and sustainability of the digital remittance market.
- Regulatory Challenges, and Compliance Requirements
Governments and regulatory bodies enforce rules to combat money laundering, terrorism financing, and other illicit activities. Compliance with these regulations presents a complex and costly challenge for remittance service providers, requiring them to implement robust compliance measures, conduct thorough customer due diligence, and maintain extensive reporting systems. The necessity to navigate these compliance challenges and ensure regulatory adherence can impede the growth and expansion of digital remittance services.
Key Trends and Opportunities to Look at
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Integration
The incorporation of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies into the digital remittance market is creating exciting opportunities for advancement and expansion. Blockchain's decentralised and immutable ledger system provides heightened security, transparency, and traceability, fostering trust among users seeking reliable and secure cross-border transaction solutions. This, in turn, accelerates market adoption.
Cryptocurrencies, especially stablecoins, offer the potential for swift and cost-effective international transfers, bypassing traditional intermediaries like banks. This can result in more competitive pricing and faster transaction settlements, addressing longstanding issues associated with traditional remittance methods.
Moreover, the flexibility of blockchain and cryptocurrencies enables providers to reach previously underserved markets with limited banking infrastructure, significantly enhancing the market's accessibility and global reach. As these technologies mature and gain acceptance, digital remittance companies that embrace them can differentiate themselves, attract tech-savvy customers, and create new revenue streams, strategically positioning themselves for success in this rapidly evolving industry.
- Efforts to Enhance Security During Digital Money Transfer
Several startups have emerged with software and applications aimed at streamlining international remittance processes, reducing both time and cost while enhancing user-friendliness. Examples include TransferWise and Wave, which prioritize encrypting financial messages to safeguard user data from potential hackers. Wave, in particular, focuses on various aspects of security such as data security, mobile security, fraud prevention, and bank access security. The company employs robust measures like locking consumer data with up to 256-bit TLS encryption.
In addition to startups, e-banking systems are also investing in enhancing advanced encryption standards and security models. These systems are transitioning towards utilizing a combination of fingerprint biometric scans and image verification to offer a more secure authentication mechanism. By connecting a biometric scanning dongle to the server, the system automatically verifies if the MAC address of the dongle matches the username and password of the account. Furthermore, image verification is employed, requiring users to identify images provided by their respective banks to prevent unauthorised access attempts. Moreover, banks are utilizing Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to secure sender and receiver account details, further enhancing security measures.
- Untapped Potential in Developing Markets
In numerous developing countries, substantial populations lack access to traditional banking services. However, the widespread availability of affordable smartphones and increasing internet connectivity offers a pathway to reach these underserved populations with digital remittance solutions.
By delivering convenient and cost-effective remittance services to these markets, companies have the chance to access a vast customer base and position themselves as significant contributors to the expanding digital economy. This initiative not only fosters increased financial inclusion and economic empowerment for individuals in these regions but also stimulates growth within the digital remittance market as a whole.
How Does the Regulatory Scenario Shape this Industry?
In August 2019, the Federal Reserve unveiled plans to develop a new interbank real-time gross settlement service known as the FedNowSM Service. This initiative aims to support seamless, secure, and efficient instant payments across the United States, operating 24x7x365. The service is scheduled to launch in 2023 and will be available to participating depository institutions.
Additionally, the Federal Reserve announced that the Fedwire Funds Service will adopt the ISO 20022 format, a move aimed at modernizing payment systems. Both the Reserve Banks and the Clearing House (TCH) intend to implement the ISO 20022 payment format standard for their domestic and cross-border wire payment systems.
Furthermore, there are discussions around considering the same standard for the domestic retail automated clearinghouse (ACH) system. On the international front, the Money Transfer Service Scheme (MTSS) facilitates the transfer of personal remittances from abroad to beneficiaries in India. According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), only inward personal remittances into India are permitted, including those intended for family maintenance and remittances for foreign tourists visiting India.
Outward remittances from India are not allowed under this scheme. The introduction of FedNowSM aims to provide seamless, secure, and efficient real-time payments in the US, improving domestic remittance transactions. The adoption of ISO 20022 by Fedwire and others modernizes payment systems, streamlining cross-border remittances for greater interoperability and simplicity
Fairfield’s Ranking Board
Top Segments
- Outward Digital Remittance Dominant
The outward digital remittance segment dominated the market in 2023. Individuals residing in foreign nations are sending funds back to their families for support, with the assistance of financial institutions and banks. These institutions prioritize swift and secure transfer services, while also striving to minimize fees and expand their clientele base. International banks and financial entities ensure the safety of outward remittances through a secure banking framework, thereby mitigating risks of financial detriment and fraudulent activities for both the sender and recipient.
Furthermore, the inward digital remittance category is projected to experience the fastest market growth. The expected surge in segment growth is driven by the rising acceptance of mobile payment technology for migrant money transfers. Financial institutions and banks worldwide are prioritizing the integration of real-time banking technology, particularly leveraging immediate payment service (IMPS). This technological advancement enables banks to extend their services to both resident and non-resident customers. Migrant workers are increasingly turning to wire transfer services for inward remittances due to their reputation for being the safest, quickest, and most widely embraced method of fund transfer.
- Money Transfer Operators Continue to Surge Ahead
In 2023, the money transfer operators category dominated the industry. Money transfer operators consistently offer lower transfer fees compared to banks while maintaining the same level of reliability and security. One of the key advantages they provide is the speed of transactions, with transfers being initiated promptly and processed within one to two days. The emergence of digital-first money transfer operators and the swift integration of funding and digital initiation features by established operators are anticipated to propel this sector forward in the forecast period.
The online platforms category is anticipated to grow substantially throughout the projected period. Online money transfer platforms effectively facilitate the transfer of funds between organisations and between organisations and their customers. These platforms enable users to directly access and easily execute money transactions. Many online money transfer platforms prioritize providing user-friendly services to their clients, aiding them in navigating their platforms effortlessly. Additionally, the rising adoption of digital wallets is anticipated to further drive growth in this sector, as digital wallets allow customers to conveniently monitor their funds through dedicated applications.
- Personal End User Leads the Way
The personal segment dominated the market in 2023. Numerous new products and services are being extensively crafted to enhance the convenient utilisation of financial customer accounts. Furthermore, the surge in global migration is projected to fuel the uptake of digital remittance services among individuals seeking to send money to their home countries. The expanding penetration of smartphones and the internet worldwide is expected to drive growth in the personal segment throughout the forecast period. Innovative solutions are already reshaping the landscape of remittance services by enhancing convenience and lowering costs for senders of remittances and their families.
The migrant labour workforce category is expected to experience the fastest growth within the forecast time frame. The digital remittance service aids migrant labourers in comparing transfer costs and efficiently identifying support organisations. Additionally, this service has simplified and made sending money home more cost-effective for migrant workers. Developments in fintech and innovations in cross-border payments are anticipated to continue driving growth in this segment. Furthermore, despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, migrant labourers persisted in their efforts to earn money for their families, thereby contributing to the growth of the segment.
Regional Frontrunners
Asia Pacific’s Rvenue Contribution Remains Maximum
Cross-border migration plays a pivotal role in the advancement of regional remittance services. India, China, and the Philippines are recognised as the primary recipients of remittances, with formal remittances amounting to US$165 billion annually. The World Bank reports a significant increase in the number of Indian students migrating to the United States of America (USA) in 2022, reaching 1.9 lakh from 1.25 lakh in 2021.
Canada emerged as the second most favoured destination for Indian students, nearly doubling to 1.85 lakh in 2022 from 1.02 lakh in 2021. The United Kingdom (UK) follows closely behind, with 1.32 lakh Indian students migrating in 2022 compared to just 77000 in 2021 and 25000 in 2018. Despite the proliferation of formal remittance service providers and their cost-effective offerings, many remittance transactions in the Asia Pacific region still rely on informal channels. This can be attributed to inadequate marketing and channel strategies employed by market players to directly engage with migrant labourers across different countries within and outside the region.
The significant growth in the manufacturing and IT sectors in key countries is attracting international workers, likely driving up remittance outflows from within the region. In developing economies, notable increases in the ICT-to-GDP ratio are fuelling digital money transfers and the digitisation of the banking sector. Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand are ranked among the top 10 economies with the highest ICT-to-GDP ratios. The substantial expansion of the ICT industry, coupled with ongoing efforts to enhance online payment systems and formalize the economy, is anticipated to drive growth in the regional digital money transfer and remittance market.
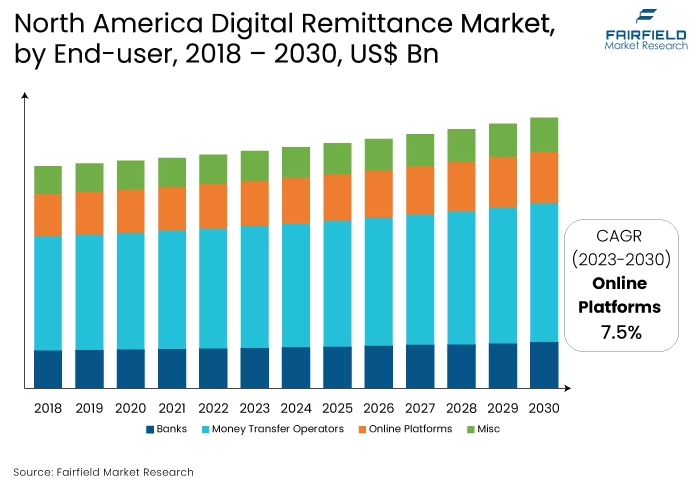
Exploding Smartphone Ownership Elevates North America’s Market Attractiveness
This growth can be attributed to several factors, including the well-established financial infrastructure of the region, high rates of internet and smartphone usage, and a sizable population of migrants who regularly send money back to their home countries. As of 2023, smartphone ownership in the United States stood at 81.6%, encompassing approximately 270 million individuals.
Americans typically spend an average of 5 hours and 24 minutes on their mobile devices each day, checking their phones around 96 times daily, roughly once every 10 minutes. Notably, smartphone ownership has risen across all age groups in the US since 2012, with a particularly significant increase among individuals aged 65 and older, climbing from 13% in 2012 to 61% in 2021. Additionally, the presence of advanced digital payment systems and a strong inclination towards technology adoption in North America has facilitated the expansion of digital remittance services.
Fairfield’s Competitive Landscape Analysis
The global digital remittance market is a consolidated market with fewer major players present across the globe. Key players are consistently prioritizing enhancements to user interfaces, integrating cutting-edge security protocols, and embracing innovations such as blockchain technology to facilitate quicker and more secure transactions. Moreover, Fairfield Market Research is expecting the market to witness more consolidation over the coming years.
Who are the Leaders in the Global Digital Remittance Space?
- Western Union
- MoneyGram International
- TransferWise
- Remitly
- WorldRemit
- Ria Financial Services
- PayPal/Xoom
- OFX
- Skrill
- Revolut
Significant Industry Developments
New Product Launch
- August 2021: In August 2021, WorldRemit Ltd. launched its money transfer operations in Malaysia, enabling users in Malaysia and over 50 other countries, such as the U.S. and the U.K., to send money to more than 130 destinations globally.
- August 2021: In August 2021, Sable, a prominent shipping fintech platform facilitating comprehensive financial solutions for global citizens lacking a credit history or an SSN, launched a new integration with Wise. This integration permits customers to conduct faster and more cost-effective international money transfers directly through Sable.
Distribution Agreement
- May 2022: In 2022, Western Union made a significant move by acquiring Uphold, a digital currency exchange. This strategic acquisition positions Western Union to expand its range of remittance options, particularly by introducing cryptocurrency choices for its customer base.
- February 2022: In 2022, PayPal bolstered its digital remittance services through the acquisition of Curv, a digital asset security firm. This move enhances PayPal's security capabilities, thereby improving the safety of its digital remittance offerings.
- January 2023: In January 2023, Xoom forged a strategic partnership with Visa Direct, allowing debit card users in 25 countries such as Thailand, the Philippines, Vietnam, Ukraine, and Sri Lanka to access funds within minutes
An Expert’s Eye
Demand and Future Growth
As per Fairfield’s Analysis, In recent years, the digital remittance sector has undergone significant advancements, reshaping the way money is sent and received across borders. A key evolution is the widespread embrace of mobile technology and internet connectivity, fuelling the proliferation of digital remittance platforms and services. Mobile applications and online platforms have simplified the process of initiating remittance transactions, eliminating the necessity for physical visits to conventional outlets.
Furthermore, progress in financial technology has facilitated swifter and more secure remittance procedures. Notably, blockchain technology has emerged as a prominent tool in the remittance domain, offering transparent and efficient transaction tracking alongside robust data security measures.
Additionally, the ascent of digital wallets and mobile payment systems has transformed the remittance landscape by providing convenient and cost-effective solutions. These platforms enable users to store and transfer funds digitally, diminishing dependence on traditional banking infrastructures. Regulatory advancements have been instrumental in shaping the digital remittance market. Many nations have acknowledged the potential of digital remittances and have introduced supportive regulations to promote innovation and competition while safeguarding consumer interests.
Supply Side of the Market
According to our analysis, Major players in the digital remittances market are concentrating on offering digital solutions, such as digital remittance services, to streamline the process of digital money transfers and gain a competitive advantage. Digital remittance services provide a secure and efficient electronic platform for transferring money across borders.
For example, in July 2023, TNG Digital Sdn Bhd, an e-wallet operator based in Malaysia, introduced GOremit, a digital remittance service integrated into the Touch 'n Go eWallet. This service allows users to send money securely, with senders undergoing electronic Know Your Customer (KYC) verification. They can select to transfer funds to the recipient's bank account, local eWallet, or designated cash pick-up points. Typically, recipients receive the transferred funds within 15 minutes.
Global Digital Remittance Market is Segmented as Below:
By Type:
- Inward Digital Remittance
- Outward Digital Remittance
By Channel:
- Banks
- Money Transfer Operators
- Online Platforms
- Misc
By End Use:
- Migrant Labour Workforce
- Personal
- Small Businesses
- Misc
By Geographic Coverage:
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Turkey
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Egypt
- Nigeria
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
1. Executive Summary
1.1. Global Digital Remittance Market Snapshot
1.2. Future Projections
1.3. Key Market Trends
1.4. Regional Snapshot, by Value, 2022
1.5. Analyst Recommendations
2. Market Overview
2.1. Market Definitions and Segmentations
2.2. Market Dynamics
2.2.1. Drivers
2.2.2. Restraints
2.2.3. Market Opportunities
2.3. Value Chain Analysis
2.4. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
2.5. Covid-19 Impact Analysis
2.5.1. Supply
2.5.2. Demand
2.6. Impact of Ukraine-Russia Conflict
2.7. Economic Overview
2.7.1. World Economic Projections
2.8. PESTLE Analysis
3. Global Digital Remittance Market Outlook, 2018 - 2030
3.1. Global Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
3.1.1. Key Highlights
3.1.1.1. Inward Digital Remittance
3.1.1.2. Outward Digital Remittance
3.2. Global Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
3.2.1. Key Highlights
3.2.1.1. Banks
3.2.1.2. Money Transfer Operators
3.2.1.3. Online Platforms
3.2.1.4. Misc
3.3. Global Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
3.3.1. Key Highlights
3.3.1.1. Migrant Labor Workforce
3.3.1.2. Personal
3.3.1.3. Small Businesses
3.3.1.4. Misc
3.4. Global Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Region, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
3.4.1. Key Highlights
3.4.1.1. North America
3.4.1.2. Europe
3.4.1.3. Asia Pacific
3.4.1.4. Latin America
3.4.1.5. Middle East & Africa
4. North America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, 2018 - 2030
4.1. North America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.1.1. Key Highlights
4.1.1.1. Inward Digital Remittance
4.1.1.2. Outward Digital Remittance
4.2. North America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.2.1. Key Highlights
4.2.1.1. Banks
4.2.1.2. Money Transfer Operators
4.2.1.3. Online Platforms
4.2.1.4. Misc
4.3. North America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.3.1. Key Highlights
4.3.1.1. Migrant Labor Workforce
4.3.1.2. Personal
4.3.1.3. Small Businesses
4.3.1.4. Misc
4.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
4.4. North America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.1. Key Highlights
4.4.1.1. U.S. Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.1.2. U.S. Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.1.3. U.S. Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.1.4. Canada Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.1.5. Canada Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.1.6. Canada Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
4.4.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
5. Europe Digital Remittance Market Outlook, 2018 - 2030
5.1. Europe Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.1.1. Key Highlights
5.1.1.1. Inward Digital Remittance
5.1.1.2. Outward Digital Remittance
5.2. Europe Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.2.1. Key Highlights
5.2.1.1. Banks
5.2.1.2. Money Transfer Operators
5.2.1.3. Online Platforms
5.2.1.4. Misc
5.3. Europe Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.3.1. Key Highlights
5.3.1.1. Migrant Labor Workforce
5.3.1.2. Personal
5.3.1.3. Small Businesses
5.3.1.4. Misc
5.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
5.4. Europe Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1. Key Highlights
5.4.1.1. Germany Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.2. Germany Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.3. Germany Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.4. U.K. Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.5. U.K. Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.6. U.K. Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.7. France Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.8. France Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.9. France Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.10. Italy Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.11. Italy Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.12. Italy Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.13. Turkey Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.14. Turkey Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.15. Turkey Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.16. Russia Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.17. Russia Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.18. Russia Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.19. Rest of Europe Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.20. Rest of Europe Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.1.21. Rest of Europe Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
5.4.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
6. Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market Outlook, 2018 - 2030
6.1. Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.1.1. Key Highlights
6.1.1.1. Inward Digital Remittance
6.1.1.2. Outward Digital Remittance
6.2. Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.2.1. Key Highlights
6.2.1.1. Banks
6.2.1.2. Money Transfer Operators
6.2.1.3. Online Platforms
6.2.1.4. Misc
6.3. Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.3.1. Key Highlights
6.3.1.1. Migrant Labor Workforce
6.3.1.2. Personal
6.3.1.3. Small Businesses
6.3.1.4. Misc
6.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
6.4. Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1. Key Highlights
6.4.1.1. China Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.2. China Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.3. China Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.4. Japan Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.5. Japan Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.6. Japan Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.7. South Korea Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.8. South Korea Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.9. South Korea Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.10. India Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.11. India Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.12. India Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.13. Southeast Asia Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.14. Southeast Asia Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.15. Southeast Asia Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.16. Rest of Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.17. Rest of Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.1.18. Rest of Asia Pacific Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
6.4.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
7. Latin America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, 2018 - 2030
7.1. Latin America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.1.1. Key Highlights
7.1.1.1. Inward Digital Remittance
7.1.1.2. Outward Digital Remittance
7.2. Latin America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.2.1. Key Highlights
7.2.1.1. Banks
7.2.1.2. Money Transfer Operators
7.2.1.3. Online Platforms
7.2.1.4. Misc
7.3. Latin America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.3.1. Key Highlights
7.3.1.1. Migrant Labor Workforce
7.3.1.2. Personal
7.3.1.3. Small Businesses
7.3.1.4. Misc
7.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
7.4. Latin America Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1. Key Highlights
7.4.1.1. Brazil Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.2. Brazil Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.3. Brazil Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.4. Mexico Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.5. Mexico Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.6. Mexico Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.7. Argentina Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.8. Argentina Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.9. Argentina Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.10. Rest of Latin America Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.11. Rest of Latin America Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.1.12. Rest of Latin America Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
7.4.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
8. Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market Outlook, 2018 - 2030
8.1. Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.1.1. Key Highlights
8.1.1.1. Inward Digital Remittance
8.1.1.2. Outward Digital Remittance
8.2. Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.2.1. Key Highlights
8.2.1.1. Banks
8.2.1.2. Money Transfer Operators
8.2.1.3. Online Platforms
8.2.1.4. Misc
8.3. Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.3.1. Key Highlights
8.3.1.1. Migrant Labor Workforce
8.3.1.2. Personal
8.3.1.3. Small Businesses
8.3.1.4. Misc
8.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
8.4. Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1. Key Highlights
8.4.1.1. GCC Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.2. GCC Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.3. GCC Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.4. South Africa Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.5. South Africa Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.6. South Africa Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.7. Egypt Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.8. Egypt Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.9. Egypt Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.10. Nigeria Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.11. Nigeria Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.12. Nigeria Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.13. Rest of Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market by Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.14. Rest of Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market Channel, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.1.15. Rest of Middle East & Africa Digital Remittance Market End Use, Value (US$ Mn), 2018 - 2030
8.4.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
9. Competitive Landscape
9.1. End Use vs Channel Heatmap
9.2. Manufacturer vs Channel Heatmap
9.3. Company Market Share Analysis, 2022
9.4. Competitive Dashboard
9.5. Company Profiles
9.5.1. Western Union
9.5.1.1. Company Overview
9.5.1.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.1.3. Financial Overview
9.5.1.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.2. MoneyGram International
9.5.2.1. Company Overview
9.5.2.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.2.3. Financial Overview
9.5.2.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.3. TransferWise
9.5.3.1. Company Overview
9.5.3.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.3.3. Financial Overview
9.5.3.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.4. Remitly
9.5.4.1. Company Overview
9.5.4.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.4.3. Financial Overview
9.5.4.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.5. WorldRemit
9.5.5.1. Company Overview
9.5.5.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.5.3. Financial Overview
9.5.5.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.6. Ria Financial Services
9.5.6.1. Company Overview
9.5.6.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.6.3. Financial Overview
9.5.6.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.7. PayPal/Xoom
9.5.7.1. Company Overview
9.5.7.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.7.3. Financial Overview
9.5.7.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.8. OFX
9.5.8.1. Company Overview
9.5.8.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.8.3. Financial Overview
9.5.8.4. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.9. Skrill
9.5.9.1. Company Overview
9.5.9.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.9.3. Business Strategies and Development
9.5.10. Revolut
9.5.10.1. Company Overview
9.5.10.2. Product Portfolio
9.5.10.3. Financial Overview
9.5.10.4. Business Strategies and Development
10. Appendix
10.1. Research Methodology
10.2. Report Assumptions
10.3. Acronyms and Abbreviations
|
BASE YEAR |
HISTORICAL DATA |
FORECAST PERIOD |
UNITS |
|||
|
2022 |
|
2018 - 2022 |
2023 - 2030 |
Value: US$ Million |
||
|
REPORT FEATURES |
DETAILS |
|
Type Coverage |
|
|
Channel Coverage |
|
|
End Use Coverage |
|
|
Geographical Coverage |
|
|
Leading Companies |
|
|
Report Highlights |
Key Market Indicators, Macro-micro economic impact analysis, Technological Roadmap, Key Trends, Driver, Restraints, and Future Opportunities & Revenue Pockets, Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis, Historical Trend (2019-2021), Market Estimates and Forecast, Market Dynamics, Industry Trends, Competition Landscape, Category, Region, Country-wise Trends & Analysis, COVID-19 Impact Analysis (Demand and Supply Chain) |
