Global Underground Mining Market Forecast
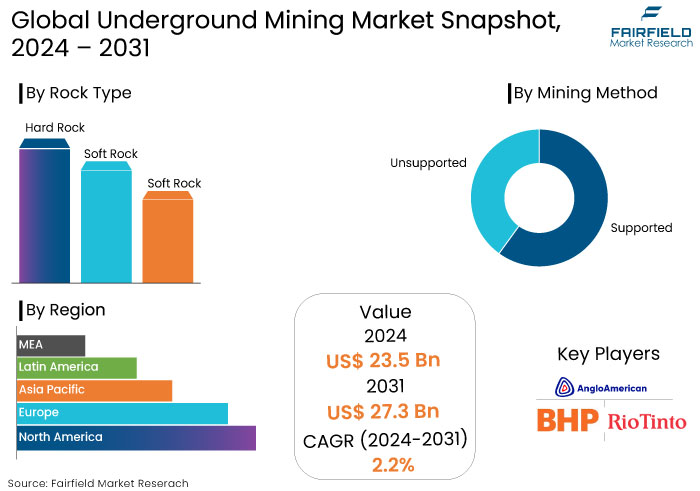
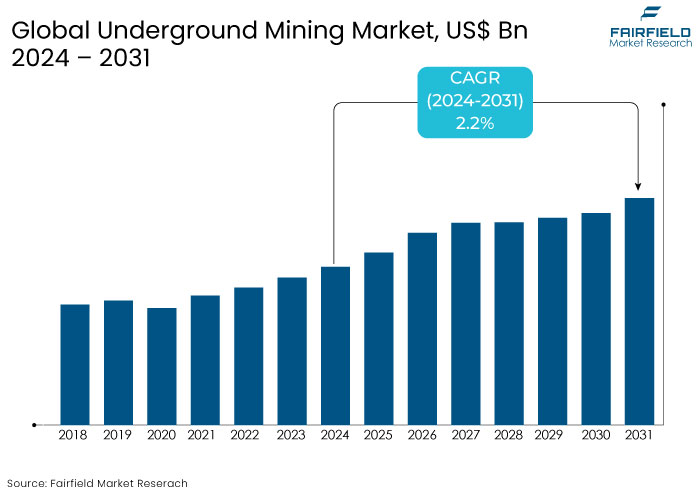
- The underground mining market is projected to reach a size of US$27.3 Bn by 2031, showing significant growth from the US$23.5 Bn achieved in 2024.
- The market for underground mining is expected to show a significant expansion rate, with an estimated CAGR of 2.2% from 2024 to 2031.
Underground Mining Market Insights
- The market is projected to expand due to rising demand for minerals and metals across various industries, particularly energy and technology.
- Innovations in automation, AI, and IoT are enhancing operational efficiency and safety, leading to increased productivity.
- A growing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices, including using electric and hybrid mining equipment to reduce emissions.
- Emerging markets especially in Africa and Latin America, are becoming focal points for exploration and development due to rich mineral deposits.
- The surging demand for essential metals such as copper, nickel, and rare earth elements is reshaping the underground mining market.
- Increasing private equity and venture capital interest in mining technology and sustainable practices creates new investment avenues.
- The industry faces a skilled labour shortage necessitating investments in training and development programs to ensure a competent workforce.
- Strict environmental and safety regulations shape mining operations pushing companies toward sustainable practices.
A Look Back and a Look Forward - Comparative Analysis
The underground mining market has experienced steady growth up to 2023, driven by the increasing demand for minerals and metals across various construction, energy, and electronics industries.
Before 2023, the market witnessed a significant rise in the adoption of mechanized and automated mining equipment, a trend that is expected to continue. Advancements have improved productivity and reduced operational costs, paving the way for a more efficient and cost-effective future.
The introduction of real-time monitoring systems and the increasing use of electric mining vehicles, driven by stringent environmental regulations have also played a crucial role in the expansion of the market. Geographically, key markets like China, Australia, and South Africa remained dominant due to abundant natural resources and large-scale mining operations.
Post-2024, the underground mining market is expected to grow further, fueled by the increased demand for rare earth metals and minerals in renewable energy technologies, electric vehicles (EVs), and battery storage systems.
The global shift towards sustainability is likely to accelerate the adoption of environmentally friendly mining practices, including using green technologies such as electric and hybrid mining machinery. Advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and robotics are projected to enhance operational efficiency and worker safety, further driving market growth.
Key Growth Determinants
- Increased Revenue from Mining Boosts Investments in the Market
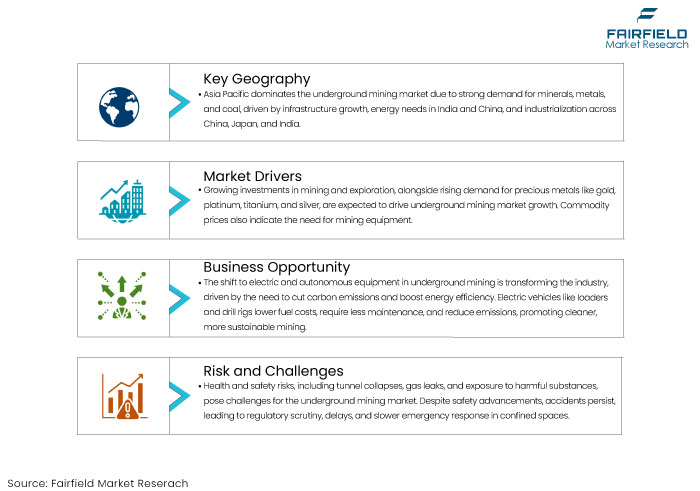
Increased investments in mining and exploration activities are anticipated to be a primary component driving revenue growth in the underground mining market.
The increasing demand for precious metals, including gold, platinum, titanium, and silver, is anticipated to stimulate the necessity for additional underground mining projects. Key commodity prices serve as the most reliable indicators of mining activity, hence reflecting the need for mining equipment.
An increase in demand is anticipated due to underground mining of metals like copper, nickel, zinc, and iron ore. From 2016 to 2018, the global metal yield experienced an increase of approximately 2-4%, enhancing the incentive for additional investment in underground mining activities and elevating the growth prospects for the market.
- Increased Demand for Metals and Minerals in Energy Transition
One of the primary growth drivers for the underground mining market is the rising demand for metals and minerals essential for the global energy transition. With the increasing adoption of renewable energy technologies, electric vehicles (EVs), and battery storage systems, minerals such as copper, lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements are becoming critical.
Underground mining, which is often efficient in extracting these minerals from deep ore bodies, is positioned to meet this rising demand. Governments worldwide are setting targets for carbon neutrality, increasing the need for renewable energy infrastructure, which significantly relies on mined materials. For instance, copper, used extensively in electrical wiring, and lithium, a key component in batteries, are projected to see significant growth in demand.
As surface deposits of these minerals deplete, underground mining operations will expand to exploit deeper resources, making this sector pivotal to supporting the green energy shift.
Key Growth Barriers
- Health and Safety Concerns
Health and safety concerns remain a significant restraint for the underground mining market. Mining operations are inherently hazardous, with risks such as tunnel collapses, gas leaks, equipment failures, and exposure to harmful dust and chemicals.
Despite advances in safety technology, accidents and fatalities still occur, leading to heightened regulatory scrutiny and operational delays. In underground environments, where space is confined, the likelihood of accidents can increase, and emergency response times may be slower compared to surface mining.
Mining companies must invest heavily in safety training, equipment, and monitoring systems to mitigate these risks, which can add to operational costs. Furthermore, accidents can lead to lengthy shutdowns, regulatory fines, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Strict safety regulations, especially in developed markets, impose additional compliance costs and can slow down the approval of new mining projects, thus acting as a restraint for the underground mining sector growth
- High Capital and Operational Costs
One of the key restraints for the underground mining market is the high capital and operational costs associated with developing and maintaining underground mining infrastructure. Unlike surface mining, underground mining requires extensive tunnelling, ventilation systems, safety measures, and specialized equipment, significantly increasing upfront investment.
The operational costs remain high due to the need for continuous maintenance of tunnels, reinforcement, and monitoring of underground conditions to prevent accidents. The labour costs are elevated as skilled workers are required to operate complex machinery in challenging environments. These high costs make underground mining less attractive for smaller companies and projects where the resource value does not justify the investment.
In many regions, fluctuating commodity prices and uncertain returns can make it difficult for companies to secure financing for underground mining operations, thereby limiting market expansion, particularly in volatile economic climates.
Underground Mining Market Trends and Opportunities
- Adoption of Electric and Autonomous Mining Equipment
One of the most transformative opportunities in the underground mining market is adopting electric and autonomous mining equipment. The shift toward electrification is driven by the global push to reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency in mining operations.
Electric-powered vehicles and machinery, such as electric loaders, trucks, and drill rigs, offer significant advantages over their diesel counterparts, including reduced fuel costs, lower maintenance needs, and a significant reduction in harmful emissions, making underground mines cleaner and more sustainable.
In addition to environmental benefits, electric equipment improves ventilation requirements, as diesel-powered machinery produces exhaust fumes that necessitate costly and energy-intensive ventilation systems in underground settings.
The rise of autonomous mining equipment is revolutionizing underground operations by enhancing productivity and safety. Autonomous haulage systems, remote-controlled equipment, and AI-driven mining processes enable more efficient resource extraction with minimal human presence in hazardous zones. This not only increases operational efficiency but also reduces the risk of accidents, making underground mining more attractive and cost-effective in the long term.
- Digitization and Real-Time Data Analytics
The increasing digitization of mining operations presents a major opportunity for underground mining market players. Mining companies can gain valuable insights into mine conditions, equipment performance, and worker safety by leveraging real-time data analytics, sensors, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
Smart mining solutions allow for real-time monitoring of underground environments, including temperature, gas levels, and structural integrity, enabling operators to detect issues early and take preventive measures. This digital transformation also extends to predictive maintenance, where data analytics can forecast equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and lowering maintenance costs.
Enhanced data collection through underground sensors and connected devices allows for precise mapping of ore bodies and more efficient resource extraction, minimizing waste and maximizing profitability.
As mining operations become more data-driven, the use of cloud platforms and advanced software solutions can further streamline processes, improving decision-making and boosting overall productivity.
How Does Regulatory Scenario Shape the Industry?
The regulatory scenario plays a pivotal role in shaping the underground mining market, particularly regarding environmental impact, worker safety, and operational efficiency. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly enforcing stricter environmental regulations to mitigate the ecological footprint of mining activities.
Underground mining, seen as more environmentally sustainable than surface mining due to its reduced land disruption, is gaining preference under these regulations. Miners are required to comply with mandates related to reducing carbon emissions, controlling water usage, and minimizing toxic waste discharge, driving the adoption of cleaner technologies such as electric machinery and improved ventilation systems.
Worker safety regulations are also evolving requiring companies to invest in better safety equipment, real-time monitoring systems, and robust emergency protocols to minimize risks associated with hazardous underground conditions. Compliance with these safety standards, including regular inspections and certifications adds operational costs and improves overall safety and efficiency.
Governments in resource-rich emerging markets are offering favourable policies and incentives to attract investment, while developed regions enforce stringent regulations, both of which are reshaping how underground mining operations are conducted globally. These regulations ultimately push the industry toward more sustainable and technologically advanced mining practices.
Segments Covered in the Report
- Hard Rock Type Takes the Lead with Increased Demand for Metals & Minerals
Hard rock mining is extracting valuable minerals or metals from solid rock formations, typically found in deep underground deposits. This method is used for mining valuable resources such as gold, copper, silver, zinc, nickel, and uranium primarily located in hard rock environments.
The dominance of the hard rock segment is driven by the crucial role it plays in meeting the increasing global demand for metals and minerals that are essential for a variety of industries. These industries include electronics, renewable energy, and electric vehicles. These industries rely heavily on materials like copper and lithium, which are extracted from hard rock deposits.
As surface-level resources become depleted, mining companies are demonstrating their innovation and adaptability by turning to deep, hard-to-reach underground deposits, further boosting the demand for hard rock mining techniques.
Hard rock mining typically requires more advanced and specialized equipment such as drill rigs, explosives, and crushing systems, which drives investment in the sector. Hard rock deposits' complexity and higher yields contribute to this segment's leading position in the underground mining market.
- Unsupported Mining Method Dominates with Cost Effectiveness
Unsupported mining methods involve extracting minerals or ores without using artificial supports to stabilize the surrounding rock formations. This approach is primarily used in cases where the rock is strong enough to maintain its stability after excavation, making it a cost-effective option.
Unsupported mining methods require less infrastructure investment than supported mining techniques, often relying on expensive reinforcement systems such as timber, concrete, or steel supports. It reduces overall operational costs, making it attractive to mining companies looking to maximize profitability, especially in large-scale operations.
Unsupported mining methods are widely used to extract valuable minerals and metals, including gold, copper, and iron ore. Block caving, for example, is particularly effective for mining large, deep ore bodies, where the natural collapse of rock helps in the extraction process. Room-and-pillar mining is commonly used for softer minerals, such as coal and potash, where large voids can be safely left behind without immediate collapse.
Regional Analysis
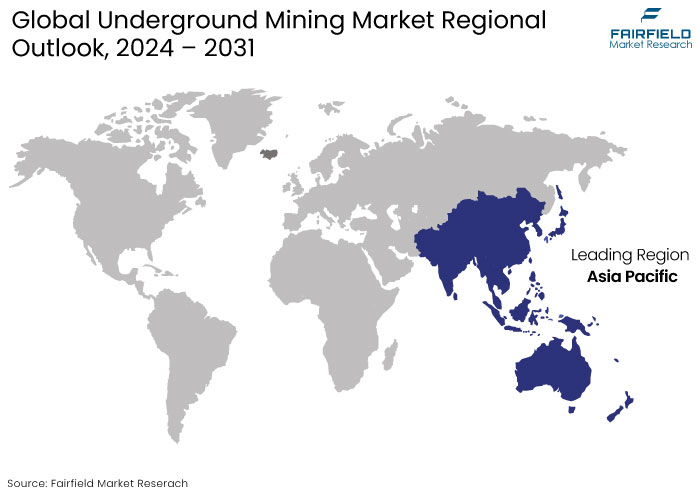
- Asia Pacific Emerges Out Dominant Regional Market
Asia Pacific leads the underground mining market, holding the significant market share because of the need for minerals, metals, and coal, alongside infrastructure development.
The increasing energy requirements of developing economies like India and China and the need for raw materials significantly contribute to market expansion. Robust population growth, industrialization, and heightened demand for minerals and metals from China, Japan, and India are propelling the expansion of the Asia Pacific market.
China ranks among the foremost global producers and consumers of coal and diverse metals, propelling the demand for underground mining apparatus inside the nation. China market encompasses a range of machinery and equipment utilized for underground mining activities.
The increase in population propels infrastructure-building initiatives particularly in developing nations like China, India, Brazil, and the Middle East resulting in advancements in the mining equipment sector.
Fairfield’s Competitive Landscape Analysis
The underground mining market is highly competitive, driven by key players focusing on technological advancements, operational efficiency, and sustainability.
Leading companies such as Rio Tinto, BHP, Glencore, Anglo-American, and Vale dominate the market through extensive global operations and strong financial resources. These companies are investing heavily in automation, electrification of mining equipment, and digital solutions to enhance productivity and reduce environmental impact.
Smaller players and regional firms compete by specializing in niche segments or providing innovative solutions such as AI-driven mine management systems and autonomous machinery.
Collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions are common strategies to expand market presence and access new technologies. Increasing regulatory pressures and sustainability goals are also pushing companies to adopt greener mining practices, influencing the competitive dynamics.
Key Market Companies
- Anglo American Plc
- BHP
- Rio Tinto
- Vale
- Alcoa Corporation
- Norilsk Nickel
- Glencore
- Codelco
- Jitegemee Holdings Company
- Barminco
- GBF Underground Mining Company
- OZ Minerals
- Jiangxi Copper
Recent Industry Developments
- March 2023 -
Sandvik launched Toro™ LH518iB with AutoMine, an automation-ready battery-electric underground loader comparable with the AutoMine automation system.
- March 2023 -
Rajant Corporation, the developer of Kinetic Mesh wireless networks, collaborated with Swedish OEM Sandvik to trial a wireless communication system that can be used with tele-remote and autonomous vehicles destined for the De Beers Venetia diamond mine.
- February 2023 -
Sandvik completed the acquisition of Polymathian Industrial Mathematics, an Australian mine optimization software provider.
An Expert’s Eye
- Automation and electrification of mining equipment will revolutionize underground mining enhancing efficiency and safety and reducing environmental impact.
- Increasing global pressure to adopt sustainable mining practices drives the shift toward electric and hybrid machinery especially in environmentally sensitive operations.
- With surface resources exhausted, experts expect deep underground mining to become the primary source of essential minerals like copper, lithium, and rare earths.
- Regions like Africa and Latin America, rich in untapped mineral reserves are seen as high-potential growth areas due to increased investment in mining infrastructure.
Global Underground Mining Market is Segmented as-
By Rock Type
- Hard Rock
- Soft Rock (Coal)
- Soft Rock (Minerals)
By Mining Method
- Supported
- Unsupported
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
1. Executive Summary
1.1. Global Underground Mining Market: Snapshot
1.2. Future Projections, 2019-2023, (US$ Mn)
1.3. Key Segment Analysis and Competitive Insights
1.4. Premium Insights
2. Market Overview
2.1. Market Definitions and Segmentation
2.2. Market Dynamics
2.2.1. Driver
2.2.1.1. Open-pit mines are becoming deeper, it becomes difficult to mine high grade ores, haulage cost of overburden will increase
2.2.1.2. Driver 2
2.2.2. Restraint
2.2.2.1. Stringent environmental regulations
2.3. Industry Challenges & Opportunities
2.4. Value Chain Analysis
2.5. Porters Five Forces Analysis
2.6. Challenges and Solutions
2.7. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
2.8. Pre and Post Covid-19 Analysis
2.9. Regulatory Scenario
2.10. Market Background
2.10.1. World Minerals Production Overview
2.10.2. Global Mining Exploration Spending
2.10.3. Foreign Investments
2.11. Economic Analysis
3. Price Analysis
3.1. Key Price Indicators
3.2. Factors Affecting Mining Cost
3.3. Price Analysis
4. Global Underground Mining Market Outlook, 2019 - 2031
4.1. Global Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Rock Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
4.1.1. Key Highlights
4.1.1.1. Hard Rock
4.1.1.2. Soft Rock (Coal)
4.1.1.3. Soft Rock (Minerals)
4.1.2. Market Attractiveness Analysis
4.2. Global Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Method, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
4.2.1. Key Highlights
4.2.1.1. Supported
4.2.1.1.1. Shrinkage Stoping
4.2.1.1.2. Room and Pillar
4.2.1.1.3. Cut and Fill
4.2.1.1.4. Misc.
4.2.1.2. Unsupported
4.2.1.2.1. Sublevel Caving
4.2.1.2.2. Block Caving
4.2.1.2.3. Sublevel Stoping
4.2.2. Market Attractiveness Analysis
4.3. Global Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Region, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
4.3.1. Key Highlights
4.3.1.1. North America
4.3.1.2. Europe
4.3.1.3. Asia Pacific
4.3.1.4. Latin America
4.3.1.5. Middle East & Africa
4.3.2. Market Attractiveness Analysis
5. North America Underground Mining Market Outlook, 2019 - 2031
5.1. North America Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Rock Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
5.1.1. Key Highlights
5.1.1.1. Hard Rock
5.1.1.2. Soft Rock (Coal)
5.1.1.3. Soft Rock (Minerals)
5.2. North America Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Method, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
5.2.1. Key Highlights
5.2.1.1. Supported
5.2.1.1.1. Shrinkage Stoping
5.2.1.1.2. Room and Pillar
5.2.1.1.3. Cut and Fill
5.2.1.1.4. Misc.
5.2.1.2. Unsupported
5.2.1.2.1. Sublevel Caving
5.2.1.2.2. Block Caving
5.2.1.3. Sublevel Stoping
5.3. North America Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
5.3.1. Key Highlights
5.3.1.1. U.S.
5.3.1.2. Canada
6. Europe Underground Mining Market Outlook, 2019 - 2031
6.1. Europe Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Rock Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
6.1.1. Key Highlights
6.1.1.1. Hard Rock
6.1.1.2. Soft Rock (Coal)
6.1.1.3. Soft Rock (Minerals)
6.2. Europe Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Method, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
6.2.1. Key Highlights
6.2.1.1. Supported
6.2.1.1.1. Shrinkage Stoping
6.2.1.1.2. Room and Pillar
6.2.1.1.3. Cut and Fill
6.2.1.1.4. Misc.
6.2.1.2. Unsupported
6.2.1.2.1. Sublevel Caving
6.2.1.2.2. Block Caving
6.2.1.3. Sublevel Stoping
6.3. Europe Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
6.3.1. Key Highlights
6.3.1.1. Germany
6.3.1.2. France
6.3.1.3. Poland
6.3.1.4. Sweden
6.3.1.5. Turkey
6.3.1.6. Russia
6.3.1.7. Rest of Europe
6.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
7. Asia Pacific Underground Mining Market Outlook, 2019 - 2031
7.1. Asia Pacific Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Rock Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
7.1.1. Key Highlights
7.1.1.1. Hard Rock
7.1.1.2. Soft Rock (Coal)
7.1.1.3. Soft Rock (Minerals)
7.2. Asia Pacific Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Method, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
7.2.1. Key Highlights
7.2.1.1. Supported
7.2.1.1.1. Shrinkage Stoping
7.2.1.1.2. Room and Pillar
7.2.1.1.3. Cut and Fill
7.2.1.1.4. Misc.
7.2.1.2. Unsupported
7.2.1.2.1. Sublevel Caving
7.2.1.2.2. Block Caving
7.2.1.3. Sublevel Stoping
7.3. Asia Pacific Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
7.3.1. Key Highlights
7.3.1.1. China
7.3.1.2. South Korea
7.3.1.3. India
7.3.1.4. Australia
7.3.1.5. Southeast Asia
7.3.1.6. Rest of Asia Pacific
7.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
8. Latin America Underground Mining Market Outlook, 2019 - 2031
8.1. Latin America Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Rock Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
8.1.1. Key Highlights
8.1.1.1. Hard Rock
8.1.1.2. Soft Rock (Coal)
8.1.1.3. Soft Rock (Minerals)
8.2. Latin America Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Method, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
8.2.1. Key Highlights
8.2.1.1. Supported
8.2.1.1.1. Shrinkage Stoping
8.2.1.1.2. Room and Pillar
8.2.1.1.3. Cut and Fill
8.2.1.1.4. Misc.
8.2.1.2. Unsupported
8.2.1.2.1. Sublevel Caving
8.2.1.2.2. Block Caving
8.2.1.3. Sublevel Stoping
8.3. Latin America Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
8.3.1. Key Highlights
8.3.1.1. Brazil
8.3.1.2. Mexico
8.3.1.3. Chile
8.3.1.4. Rest of Latin America
8.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
9. Middle East & Africa Underground Mining Market Outlook, 2019 - 2031
9.1. Middle East & Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Rock Type, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
9.1.1. Key Highlights
9.1.1.1. Hard Rock
9.1.1.2. Soft Rock (Coal)
9.1.1.3. Soft Rock (Minerals)
9.2. Middle East & Africa Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Method, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
9.2.1. Key Highlights
9.2.1.1. Supported
9.2.1.1.1. Shrinkage Stoping
9.2.1.1.2. Room and Pillar
9.2.1.1.3. Cut and Fill
9.2.1.1.4. Misc.
9.2.1.2. Unsupported
9.2.1.2.1. Sublevel Caving
9.2.1.2.2. Block Caving
9.2.1.3. Sublevel Stoping
9.3. Middle East & Africa Underground Mining Market Outlook, by Country, Value (US$ Mn), 2019 - 2031
9.3.1. Key Highlights
9.3.1.1. GCC
9.3.1.2. South Africa
9.3.1.3. Ghana
9.3.1.4. Rest of Middle East & Africa
9.3.2. BPS Analysis/Market Attractiveness Analysis
10. Competitive Landscape
10.1. Company Market Share Analysis, 2021
10.2. Competition Matrix (By Tier and Size of companies)
10.3. Recent Transactions, by Transport Mode
10.4. Strategic Collaborations
10.4.1. Joint Ventures
10.4.2. Mergers & Acquisitions
10.5. Company Profiles
10.5.1. Anglo American Plc
10.5.1.1. Company Overview
10.5.1.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.1.3. Financial Overview
10.5.1.4. Business Strategies and Development
(*Note: Above details would be available for below list of companies based on availability)
10.5.2. BHP
10.5.2.1. Company Overview
10.5.2.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.2.3. Financial Overview
10.5.2.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.3. Rio Tinto
10.5.3.1. Company Overview
10.5.3.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.3.3. Financial Overview
10.5.3.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.4. Vale
10.5.4.1. Company Overview
10.5.4.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.4.3. Financial Overview
10.5.4.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.5. Alcoa Corporation
10.5.5.1. Company Overview
10.5.5.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.5.3. Financial Overview
10.5.5.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.6. Norilsk Nickel
10.5.6.1. Company Overview
10.5.6.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.6.3. Financial Overview
10.5.6.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.7. Glencore
10.5.7.1. Company Overview
10.5.7.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.7.3. Financial Overview
10.5.7.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.8. Codelco
10.5.8.1. Company Overview
10.5.8.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.8.3. Financial Overview
10.5.8.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.9. Jitegemee Holdings Company
10.5.9.1. Company Overview
10.5.9.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.9.3. Financial Overview
10.5.9.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.10. Barminco
10.5.10.1. Company Overview
10.5.10.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.10.3. Financial Overview
10.5.10.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.11. GBF Underground Mining Company
10.5.11.1. Company Overview
10.5.11.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.11.3. Financial Overview
10.5.11.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.12. OZ Minerals
10.5.12.1. Company Overview
10.5.12.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.12.3. Financial Overview
10.5.12.4. Business Strategies and Development
10.5.13. Jiangxi Copper
10.5.13.1. Company Overview
10.5.13.2. Product Portfolio
10.5.13.3. Financial Overview
10.5.13.4. Business Strategies and Development
11. Appendix
11.1. Acronyms and Abbreviations
11.2. Research Scope & Assumptions
11.3. Research Methodology and Information Sources
|
BASE YEAR |
HISTORICAL DATA |
FORECAST PERIOD |
UNITS |
|||
|
2023 |
|
2019 - 2023 |
2024 - 2031 |
Value: US$ Million |
||
|
REPORT FEATURES |
DETAILS |
|
Rock Type Coverage |
|
|
Mining Method Coverage |
|
|
Geographical Coverage |
|
|
Leading Market Companies |
|
|
Report Highlights |
Key Market Indicators, Macro-micro economic impact analysis, Technological Roadmap, Key Trends, Driver, Restraints, and Future Opportunities & Revenue Pockets, Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis, Historical Trend (2019-2021), Market Estimates and Forecast, Market Dynamics, Industry Trends, Competition Landscape, Category, Region, Country-wise Trends & Analysis, COVID-19 Impact Analysis (Demand and Supply Chain) |
