U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Forecast
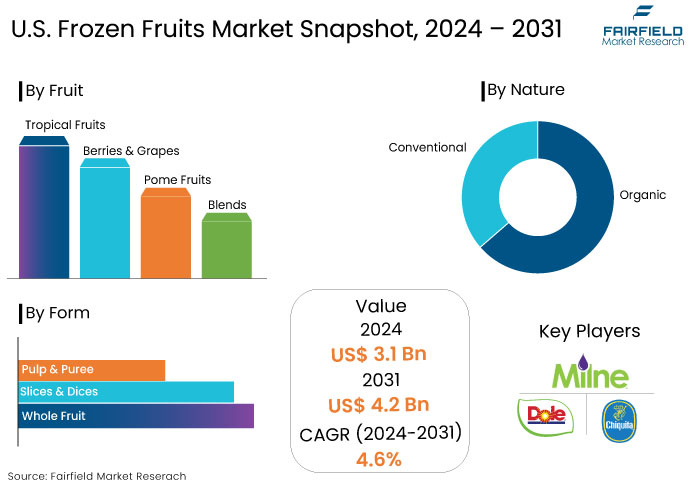
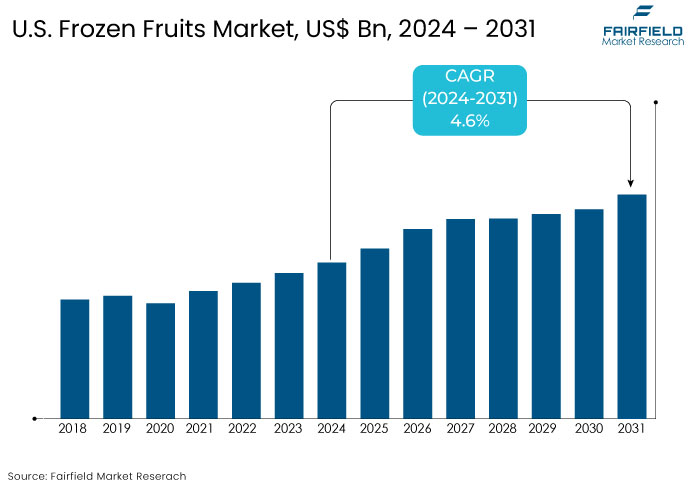
- The U.S. frozen fruits market is slated to be valued at US$4.2 Bn by 2031, showcasing significant growth from the US$3.1 Bn obtained in 2024.
- The U.S. market for frozen fruits is likely to capture a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period between 2024 and 2031.
U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Insights
- The U.S. frozen fruits market has experienced steady growth driven by rising consumer demand for year-round fruit availability and long shelf life.
- Increasing preference for convenient food products is propelling the market, especially among urban consumers and millennials.
- Consumers are increasingly focusing on nutrient-dense foods that retain vitamins and minerals, especially in response to busy lifestyles.
- Frozen fruits preserve nutrients longer compared to fresh produce, aligning with health trends.
- Smoothies and acai bowls have gained popularity across retail and food service channels, driving demand for frozen berries, mangoes, and other tropical fruits.
- The plant-based movement is also encouraging people to replace dairy-based desserts with fruit-based alternatives.
- Efficient cold chain infrastructure is essential for maintaining product quality and shelf life.
- Companies are introducing new products like frozen fruit blends, organic frozen fruits, and single-serve packs, catering to changing consumer preferences.
- The demand for frozen fruits through online grocery platforms continues to rise, driven by the increased convenience of home delivery and the expansion of grocery delivery services.
A Look Back and a Look Forward - Comparative Analysis
The U.S. frozen fruits market has evolved steadily, shaped by shifting consumer preferences towards convenience, health consciousness, and sustainability. The market gained momentum as consumers began seeking alternatives to fresh fruits that could offer extended shelf life without compromising nutritional value.
The rise of home-based meal preparation further boosted demand, particularly during periods of economic uncertainty and seasonal unavailability of fresh produce. In the forecast period, the market is expected to maintain the positive trajectory, driven by trends such as increased adoption of plant-based diets, the popularity of functional foods, and increasing consumer focus on immune health.
Advancements in freezing technologies are enhancing product quality, retaining flavor, and texture while meeting consumer demands for clean-label options with minimal additives. As online grocery platforms continue to gain traction, the availability and accessibility of frozen fruits are expected to grow.
The market future also be influenced by emerging product varieties, such as exotic fruits, and a rising focus on sustainable sourcing, aligning with growing environmental awareness.
Key Growth Determinants
- Extended Shelf Life Reducing Food Waste
Frozen fruits offer a significant advantage over fresh produce by providing an extended shelf life, which plays a vital role in reducing food waste. Unlike fresh fruits that often spoil within days, frozen fruits can maintain their nutritional value and taste for several months, thanks to flash-freezing technology. This makes them an ideal choice for eco-conscious consumers aiming to minimize waste at home.
Retailers and restaurants also benefit from reduced product spoilage, lowering disposal costs and improving inventory management. Since frozen fruits can be stored in bulk, they align with sustainable consumption practices by enabling consumers to use only what they need without worrying about spoilage.
- Rising Interest in Functional Foods
The growing consumer focus on health and wellness has fueled demand for functional foods, including frozen fruits that offer essential nutrients like antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. With rising concerns about immune health, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic, consumers are turning to foods that provide targeted health benefits.
Frozen fruits such as blueberries, acai berries, and pomegranates are increasingly popular due to their high content of antioxidants, which help reduce oxidative stress and support immunity. Similarly, vitamin-rich fruits like mangoes (vitamin A) and strawberries (vitamin C) are being sought after to promote skin health and fight infections.
Key Growth Barriers
- High Energy and Storage Costs
Seasonal dependency for raw materials significantly affects the U.S. frozen fruits market, even though freezing processes effectively extend the shelf life of these products. Frozen fruits rely on specific harvest seasons, which can create fluctuations in availability and supply consistency. For instance, crops like strawberries, blueberries, and peaches have designated harvest windows during which they are at peak quality and flavor. If adverse weather conditions, such as unexpected frosts or droughts, impact these harvests, it can lead to shortages in raw materials, disrupting production cycles.
- Volatility in Fruit Prices
Volatility in fruit prices poses a significant challenge for frozen fruit companies, directly impacting their profitability and operational stability. Various factors contribute to these price fluctuations, including unpredictable weather patterns, pest infestations, and geopolitical tensions.
Extreme weather events such as hurricanes or droughts can devastate fruit crops, resulting in reduced supply and subsequently driving up prices. Similarly, pest outbreaks can lead to extensive crop damage, further tightening the availability of raw materials.
U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Trends and Opportunities
- Expansion of E-commerce Platforms
The expansion of e-commerce platforms presents a significant opportunity for the frozen fruit companies to enhance their market reach and improve accessibility to consumers. As online grocery shopping continues to gain popularity, frozen fruit manufacturers can capitalize on this trend by establishing robust online sales channels. This shift allows to connect directly with consumers, bypassing traditional retail intermediaries and offering a personalized shopping experience.
Companies can showcase their product ranges, provide detailed nutritional information, and engage in targeted marketing campaigns by leveraging e-commerce platforms to attract health-conscious buyers. The ability to offer subscription services or bulk purchasing options can also cater to the increasing demand for convenience, making it easy for consumers to maintain a steady supply of frozen fruits.
- Technological Advancements in Freezing
Investing in technological advancements in freezing processes is crucial for frozen fruit companies aiming to enhance product quality and extend shelf life while preserving nutritional value.
Traditional freezing methods often result in cell rupture, leading to texture and flavor loss in fruits. However, innovative techniques like flash freezing and cryogenic freezing offer solutions to these challenges. Flash freezing rapidly lowers temperatures, allowing fruits to freeze quickly, which helps maintain their cellular structure and freshness. This method not only preserves the natural taste and texture of the fruits but also retains essential vitamins and minerals that might otherwise degrade during conventional freezing.

Segments Covered in the Report
- Berries & Grapes Hold Larger Share with their Widespread Popularity
Berries and grapes hold a significant share in the U.S. frozen fruits market due to their widespread popularity, versatile applications, and health benefits. Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are celebrated for their rich nutritional profiles, high antioxidant content, and low-calorie count. All these factors make them a favored choice among health-conscious consumers. Their natural sweetness and vibrant colors enhance various dishes, from smoothies and desserts to salads and sauces, further driving demand.
Grapes, particularly when frozen, serve as convenient, bite-sized snacks and can also be used in various culinary applications, including baking and cooking. The trend toward healthier snacking options has led many consumers to seek out frozen berries and grapes as alternatives to processed snacks. Additionally, the rise of plant-based diets has further bolstered the popularity of these fruits, as they are integral components in smoothies and smoothie bowls.
- Business to Business Distribution Channel Takes the Lead
Business-to-business (B2B) distribution dominates the U.S. frozen fruits market due to several key factors that align with the operational needs of large-scale buyers. One of the primary drivers is the significant demand from food service establishments, such as restaurants, cafes, and catering companies, which rely heavily on bulk purchasing to meet their operational requirements. These businesses prioritize consistent supply and quality, making B2B distribution an ideal model for sourcing frozen fruits that can be used in various dishes, desserts, and beverages.
Furthermore, B2B relationships often involve long-term contracts and partnerships, providing suppliers with stable revenue streams and predictable demand. This stability is essential for manufacturers, allowing them to optimize production processes and manage inventory effectively. Additionally, B2B distributors typically have established logistics networks, ensuring timely delivery and maintaining the cold chain necessary to preserve product quality during transit.
Zone Analysis
- Southeast U.S. Contributes Significantly to Market Expansion
The Southeast U.S. plays a pivotal role in the frozen fruits market, largely due to its favorable climatic conditions and extensive agricultural infrastructure. The region's warm, subtropical climate is ideal for cultivating a variety of fruits, including strawberries, blueberries, peaches, and blackberries, which are crucial raw materials for frozen fruit production. States like Florida and Georgia lead in fruit production, providing a consistent supply chain that supports local processing facilities and manufacturers.
The Southeast is strategically located near leading distribution channels, facilitating efficient transportation of frozen fruits to key markets across the country. The presence of established logistics networks ensures that products maintain their quality and freshness during transit, a critical factor for frozen goods.
Fairfield’s Competitive Landscape Analysis
The competitive landscape of the U.S. frozen fruits market is characterized by a blend of established players and emerging brands, each vying for market share through product innovation, strategic partnerships, and effective distribution channels. The U.S. market for frozen fruits is driven by increasing consumer demand for healthy, convenient, and year-round availability of fruits. Key players in this market range from leading frozen food companies to specialized fruit producers
Key Market Companies
- AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG (Dirafrost)
- Kerry Group plc. (Ravifruit)
- Dole Plc
- Chiquita group
- Milne Fruit Products Inc.
- ShimlaHills
- Nature's Touch.
- Meel Corporation
- SAS SICA SICODIS
- Others
Recent Industry Developments
- In October 2023, Nature's Touch, successfully acquired key assets from Sunrise Growers, the frozen fruit operations of SunOpta Inc. This strategic acquisition marked a significant milestone in Nature's Touch's expansion, reinforcing its commitment to delivering high-quality, affordable, and diverse frozen food products to consumers across Canada and the United States.
An Expert’s Eye
- The S. frozen fruits market has gained significant momentum, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenient and nutritious food options. An expert’s eye reveals a landscape ripe with opportunities, particularly as health trends continue to evolve
- Consumers are increasingly prioritizing frozen fruits due to their long shelf life, ease of use, and retention of nutrients, making them an ideal choice for smoothies, desserts, and savory dishes.
- The market is witnessing a notable shift toward organic products, reflecting a broader trend of health consciousness and a preference for clean-label foods.
- There is a rising demand for organic frozen fruits and those labelled as non-GMO with consumers becoming health-conscious.
- Frozen fruits help reduce food waste, which appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
- The demand for frozen fruits from restaurants, cafes, and smoothie bars is contributing to the market growth, especially as the foodservice industry recovers post-pandemic.
U.S. Frozen Fruits Market is Segmented as-
By Fruit Type
- Tropical Fruits
- Banana
- Mango
- Pineapple
- Papaya
- Others
- Berries & Grapes
- Strawberry
- Blueberry
- Raspberry
- Grapes
- Others
- Pome Fruits
- Apple
- Cherries
- Peaches
- Pears
- Plum
- Quince
- Blends
By Nature
- Organic
- Conventional
By Form
- Whole Fruit
- Slices & Dices
- Pulp & Puree
By End-use Industry
- Food & Beverage Industry
- Bakery & Confectionary
- Dairy & Desserts
- Beverages
- Others
- Food Service Industry
- Retail / Household
By Distribution Channel
- Business to Business
- Business to Consumer
- Hypermarkets / Supermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- Specialty Stores
- Online Retail
By Zone
- West U.S.
- Midwest U.S.
- Southwest U.S.
- Southeast U.S.
- Northeast U.S.
1. Executive Summary
1.1. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Snapshot, 2024 and 2031
1.2. Market Opportunity Assessment, 2024 - 2031, US$ Mn
1.3. Key Market Trends
1.4. Future Market Projections
1.5. Premium Market Insights
1.6. Industry Developments and Key Market Events
1.7. PMR Analysis and Recommendations
2. Market Overview
2.1. Market Scope and Definition
2.2. Market Dynamics
2.2.1. Drivers
2.2.2. Restraints
2.2.3. Opportunity
2.2.4. Challenges
2.2.5. Key Trends
2.3. Macro-Economic Factors
2.3.1. U.S. GDP Growth Outlook
2.3.2. U.S. Food and Beverage Industry Outlook
2.4. COVID-19 Impact Analysis
2.5. Forecast Factors – Relevance and Impact
3. Value Added Insights
3.1. Service Adoption Analysis
3.2. Regulatory Landscape
3.3. Key Deals and Mergers
3.4. List of Service Providers
3.5. Technology Assessment
3.6. PESTLE Analysis
3.7. Porter’s Five Force Analysis
4. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: Historical (2019 - 2023) and Forecast (2024 - 2031)
4.1. Key Highlights
4.1.1. Market Size (US$ Mn) and Y-o-Y Growth
4.1.2. Absolute $ Opportunity
4.2. Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast
4.2.1. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, 2019 - 2023
4.2.2. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, 2024 - 2031
4.3. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: Fruit Type
4.3.1. Introduction / Key Findings
4.3.2. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, By Fruit Type, 2019 - 2023
4.3.3. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, By Fruit Type, 2024 - 2031
4.3.3.1. Tropical Fruits
4.3.3.1.1. Banana
4.3.3.1.2. Mango
4.3.3.1.3. Pineapple
4.3.3.1.4. Papaya
4.3.3.1.5. Others
4.3.3.2. Berries & Grapes
4.3.3.2.1. Strawberry
4.3.3.2.2. Blueberry
4.3.3.2.3. Raspberry
4.3.3.2.4. Grapes
4.3.3.2.5. Others
4.3.3.3. Pome Fruits
4.3.3.3.1. Apple
4.3.3.3.2. Cherries
4.3.3.3.3. Peaches
4.3.3.3.4. Pears
4.3.3.3.5. Plum
4.3.3.3.6. Quince
4.3.3.4. Blends
4.4. Market Attractiveness Analysis: Fruit Type
4.5. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: Nature
4.5.1. Introduction / Key Findings
4.5.2. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, By Nature, 2019 - 2023
4.5.3. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, By Nature, 2024 - 2031
4.5.3.1. Organic
4.5.3.2. Conventional
4.6. Market Attractiveness Analysis: Nature
4.7. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: Form
4.7.1. Introduction / Key Findings
4.7.2. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, By Form, 2019 - 2023
4.7.3. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, By Form, 2024 - 2031
4.7.3.1. Whole Fruit
4.7.3.2. Slices & Dices
4.7.3.3. Pulp & Puree
4.8. Market Attractiveness Analysis: Form
4.9. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: End-use
4.9.1. Introduction / Key Findings
4.9.2. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, By End-use, 2019 - 2023
4.9.3. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, By End-use, 2024 - 2031
4.9.3.1. Food & Beverage Industry
4.9.3.1.1. Bakery & Confectionary
4.9.3.1.2. Dairy & Desserts
4.9.3.1.3. Beverages
4.9.3.1.4. Others
4.9.3.2. Food Service Industry
4.9.3.3. Retail / Household
4.10. Market Attractiveness Analysis: End-use
4.11. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: Distribution Channel
4.11.1. Introduction / Key Findings
4.11.2. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, By Distribution Channel, 2019 - 2023
4.11.3. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, By Distribution Channel, 2024 - 2031
4.11.3.1. Business to Business
4.11.3.2. Business to Consumer
4.11.3.2.1. Hypermarkets / Supermarkets
4.11.3.2.2. Convenience Stores
4.11.3.2.3. Specialty Stores
4.11.3.2.4. Online Retail
4.12. Market Attractiveness Analysis: Distribution Channel
4.13. U.S. Frozen Fruits Market Outlook: Zone
4.13.1. Introduction / Key Findings
4.13.2. Historical Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis, By Zone, 2019 - 2023
4.13.3. Current Market Size (US$ Mn) Analysis and Forecast, By Zone, 2024 - 2031
4.13.3.1. West U.S.
4.13.3.2. Midwest U.S.
4.13.3.3. Southwest U.S.
4.13.3.4. Southeast U.S.
4.13.3.5. Northeast U.S.
4.14. Market Attractiveness Analysis: Zone
5. Competition Landscape
5.1. Market Share Analysis, 2023
5.2. Market Structure
5.2.1. Competition Intensity Mapping By Market
5.2.2. Competition Dashboard
5.3. Company Profiles (Details – Overview, Financials, Strategy, Recent Developments)
5.3.1. AGRANA Beteiligungs-AG (Dirafrost)
5.3.1.1. Overview
5.3.1.2. Segments and Products
5.3.1.3. Key Financials
5.3.1.4. Market Developments
5.3.1.5. Market Strategy
5.3.2. Kerry Group plc. (Ravifruit)
5.3.2.1. Overview
5.3.2.2. Segments and Products
5.3.2.3. Key Financials
5.3.2.4. Market Developments
5.3.2.5. Market Strategy
5.3.3. Dole Plc
5.3.3.1. Overview
5.3.3.2. Segments and Products
5.3.3.3. Key Financials
5.3.3.4. Market Developments
5.3.3.5. Market Strategy
5.3.4. Chiquita group
5.3.4.1. Overview
5.3.4.2. Segments and Products
5.3.4.3. Key Financials
5.3.4.4. Market Developments
5.3.4.5. Market Strategy
5.3.5. Milne Fruit Products Inc.
5.3.5.1. Overview
5.3.5.2. Segments and Products
5.3.5.3. Key Financials
5.3.5.4. Market Developments
5.3.5.5. Market Strategy
5.3.6. ShimlaHills
5.3.6.1. Overview
5.3.6.2. Segments and Products
5.3.6.3. Key Financials
5.3.6.4. Market Developments
5.3.6.5. Market Strategy
5.3.7. Nature's Touch.
5.3.7.1. Overview
5.3.7.2. Segments and Products
5.3.7.3. Key Financials
5.3.7.4. Market Developments
5.3.7.5. Market Strategy
5.3.8. Meel Corporation
5.3.8.1. Overview
5.3.8.2. Segments and Products
5.3.8.3. Key Financials
5.3.8.4. Market Developments
5.3.8.5. Market Strategy
5.3.9. SAS SICA SICODIS
5.3.9.1. Overview
5.3.9.2. Segments and Products
5.3.9.3. Key Financials
5.3.9.4. Market Developments
5.3.9.5. Market Strategy
5.3.10. Others
5.3.10.1. Overview
5.3.10.2. Segments and Products
5.3.10.3. Key Financials
5.3.10.4. Market Developments
5.3.10.5. Market Strategy
6. Appendix
6.1. Research Methodology
6.2. Research Assumptions
6.3. Acronyms and Abbreviations
|
BASE YEAR |
HISTORICAL DATA |
FORECAST PERIOD |
UNITS |
|||
|
2023 |
|
2019 - 2023 |
2024 - 2031 |
Value: US$ Billion |
||
|
REPORT FEATURES |
DETAILS |
|
Fruit Type Coverage |
|
|
Nature Coverage |
|
|
Form Coverage |
|
|
End-use Industry Coverage |
|
|
Distribution Channel Coverage |
|
|
Zone Covered |
|
|
Leading Companies |
|
|
Report Highlights |
Key Market Indicators, Macro-micro economic impact analysis, Technological Roadmap, Key Trends, Drivers, Restraints, and Future Opportunities & Revenue Pockets, Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis, Historical Trend (2019-2021), Market Estimates and Forecast, Market Dynamics, Industry Trends, Competition Landscape, Category, Region, Country-wise Trends & Analysis, COVID-19 Impact Analysis (Demand and Supply Chain) |
